 &
&
I. Introduction
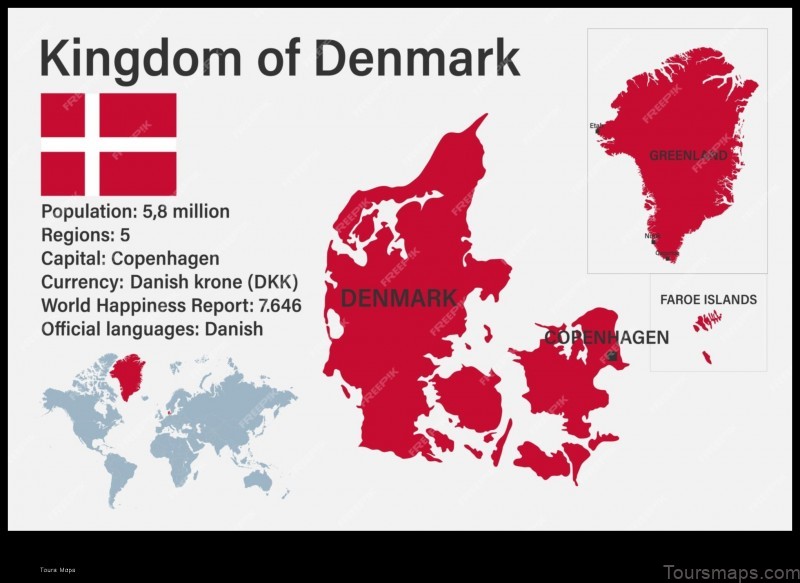
Denmark is a country located in Northern Europe. It is bordered by Germany to the south, Sweden to the east, and the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the north and west. Denmark has a population of approximately 5.8 million people and a land area of 43,094 square kilometers. The capital and largest city of Denmark is Copenhagen.

II. Map of Denmark
The following map shows the location of Denmark in Europe:
The map below shows the regions of Denmark:
III. Regions of Denmark
Denmark is divided into five regions:
- Zealand
- Funen
- Jutland
- North Jutland
- Bornholm
IV. Cities in Denmark
The following is a list of the largest cities in Denmark by population:
- Copenhagen (1.3 million)
- Aarhus (276,000)
- Odense (186,000)
- Aalborg (139,000)
- Esbjerg (105,000)
V. Landmarks in Denmark
The following is a list of some of the most famous landmarks in Denmark:
- The Little Mermaid
- Christiansborg Palace
- Roskilde Cathedral
- Legoland
- Tivoli Gardens
VI. Transportation in Denmark
The following is a list of the main forms of transportation in Denmark:
- Airplane
- Train
- Bus
- Car
- Bicycle
VII. Culture in Denmark
The following are some of the main characteristics of Danish culture:
- A strong sense of community
- A focus on equality
- A love of nature
- A taste for good food and drink
- A passion for cycling
VIII. History of Denmark
The following is a brief overview of the history of Denmark:
- The first humans arrived in Denmark around 12,000 years ago.
- The Vikings ruled Denmark from the 8th to the 11th centuries.
- Denmark became a Christian country in the 10th century.
- Denmark was a united kingdom from the 14th to the 19th centuries.
- Denmark lost Norway and Iceland in the 19th century.
- Denmark joined the European Union in 1973.
IX. Government of Denmark
The following is a brief overview of the government of Denmark:
- Denmark is a constitutional monarchy.
- The head of state is the Queen of Denmark.
- The head of government is the Prime Minister of Denmark.
- The legislature is the Folketing.
- The judiciary is independent of the
Topic Answer Map of Denmark Link to Map of Denmark Denmark Travel Link to Denmark Travel Guide Denmark Tourism Link to Denmark Tourism Guide Denmark Map Features The map of Denmark features the following:
- The Jutland Peninsula
- The Danish islands
- The Øresund Strait
- The Baltic Sea
- The North Sea
II. Map of Denmark
Denmark is a country in Northern Europe, located on the Jutland Peninsula and several islands in the North Sea. It borders Germany to the south, Sweden to the east, and Norway to the north. Denmark has a total area of 43,094 square kilometers (16,639 sq mi), making it the smallest country in the Nordic region. The country’s capital and largest city is Copenhagen.
Denmark’s landscape is varied, with a coastline that stretches for over 7,300 kilometers (4,500 mi). The country’s interior is dominated by low-lying plains, with hills and mountains in the south and east. Denmark’s climate is temperate, with mild winters and cool summers.
Denmark is a member of the European Union and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). The country’s economy is based on services, industry, and agriculture. Denmark is a popular tourist destination, with attractions such as the Tivoli Gardens, the Royal Palaces, and the Viking Ship Museum.
III. Regions of Denmark
Denmark is divided into five regions:
-
North Denmark
-
Central Denmark
-
East Denmark
-
South Denmark
-
Zealand
IV. Cities in Denmark
Denmark is home to a number of beautiful and historic cities, each with its own unique charm. Here are a few of the most popular destinations for visitors to Denmark:
- Copenhagen is the capital and largest city of Denmark. It is located on the island of Zealand and is known for its beautiful architecture, including the iconic Rundetårn (Round Tower) and the Amalienborg Palace. Copenhagen is also home to a number of museums and art galleries, as well as a vibrant nightlife scene.
- Odense is the second-largest city in Denmark and is located on the island of Funen. It is known as the birthplace of Hans Christian Andersen, and is home to a number of museums and attractions related to the famous author. Odense is also a popular tourist destination for its beautiful architecture and its many parks and gardens.
- Aarhus is the third-largest city in Denmark and is located on the island of Jutland. It is known for its lively atmosphere and its many cultural attractions, including the ARoS Aarhus Art Museum and the Moesgaard Museum. Aarhus is also a popular destination for students, as it is home to the University of Aarhus, one of the largest universities in Scandinavia.
- Roskilde is a city located on the island of Zealand. It is known for its beautiful cathedral, which is one of the oldest churches in Denmark. Roskilde is also home to a number of museums and art galleries, as well as a vibrant nightlife scene.
These are just a few of the many cities that you can visit in Denmark. Each city has its own unique charm and attractions, so be sure to do some research before you decide where to visit.
V. Landmarks in Denmark
Denmark is home to many landmarks, both natural and man-made. Some of the most popular landmarks include:
- The Little Mermaid statue, located in Copenhagen
- The Kronborg Castle, located in Helsingør
- The Roskilde Cathedral, located in Roskilde
- The Tivoli Gardens, located in Copenhagen
- The Øresund Bridge, connecting Denmark to Sweden
These are just a few of the many landmarks that Denmark has to offer. Visitors to the country will find a wealth of interesting and beautiful places to visit.
VI. Transportation in DenmarkDenmark has a well-developed transportation system that includes roads, railways, waterways, and airports. The road network is extensive and well-maintained, and there are a number of major highways that connect the country’s major cities. The railway network is also extensive, and there are a number of trains that run between Copenhagen and other major cities in Denmark. The waterways are also used for transportation, and there are a number of ferries that run between Denmark and other countries in Scandinavia. The country has three international airports: Copenhagen Airport, Billund Airport, and Aarhus Airport.
VII. Culture in Denmark
Danish culture is a blend of Scandinavian, Germanic, and Nordic influences. It is characterized by its strong sense of community, its love of nature, and its emphasis on social equality.
The Danish language is a West Germanic language closely related to Swedish and Norwegian. It is spoken by approximately 5.5 million people in Denmark, Greenland, and the Faroe Islands.
The Danish people are known for their sense of humor, their directness, and their love of food and drink. They are also very family-oriented and place a high value on education.
Danish culture is reflected in the country’s many museums, art galleries, and theaters. It is also evident in the traditional Danish cuisine, which includes dishes such as smørrebrød (open-faced sandwiches), frikadeller (Danish meatballs), and stegt flæsk (fried pork belly).
Denmark is a multicultural country, and its culture is influenced by the many immigrants who have settled there. This diversity has made Denmark a vibrant and cosmopolitan society.
History of Denmark
The history of Denmark is a long and complex one, dating back to the Stone Age. The first known inhabitants of Denmark were hunter-gatherers who lived in small settlements along the coast. Around 4000 BC, the first farmers arrived in Denmark, bringing with them new technologies and skills. During the Bronze Age (1800-500 BC), Denmark was a major trading hub, with links to other parts of Europe and the Mediterranean. The Iron Age (500 BC-AD 800) saw the rise of the Danish Vikings, who were famous for their seafaring skills and their raids on other countries. In the 10th century, Denmark was converted to Christianity, and in the 11th century, the Danish king, Canute the Great, ruled over a vast empire that included England, Norway, and parts of Sweden. In the 13th century, Denmark was hit by a series of wars and plagues, which weakened the country’s economy and power. In the 15th century, Denmark was ruled by the Kalmar Union, which also included Norway and Sweden. However, the union was dissolved in the 16th century, and Denmark entered a period of decline. In the 17th century, Denmark was involved in a series of wars with Sweden, which resulted in the loss of some of Denmark’s territory. In the 18th century, Denmark experienced a period of economic growth and prosperity. However, in the 19th century, Denmark was once again involved in a series of wars, which led to the loss of Norway. In the 20th century, Denmark was neutral during World War I and World War II. After the war, Denmark became a member of the United Nations and the European Union. Today, Denmark is a prosperous and democratic country with a high standard of living.
IX. Government of Denmark
The government of Denmark is a unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy. The monarch is the head of state, but the executive power is exercised by the prime minister and the cabinet. The legislative power is vested in the unicameral Folketing.
The Folketing consists of 179 members who are elected for four-year terms. The members are elected by proportional representation from multi-member constituencies.
The prime minister is appointed by the monarch and must have the support of the Folketing. The prime minister and the cabinet are responsible to the Folketing.
The government of Denmark is responsible for the administration of the country and for the formulation of policies. The government also represents Denmark in international affairs.
The government of Denmark is a stable and democratic government. Denmark is a member of the European Union and NATO.
X. FAQ
Q: What is the capital of Denmark?
A: Copenhagen
Q: What are the major languages spoken in Denmark?
A: Danish, Faroese, Greenlandic
Q: What is the currency of Denmark?
A: Danish krone
Table of Contents
Maybe You Like Them Too
- Explore Angleton, Texas with this detailed map
- Explore Blavozy, France with this detailed map
- Explore East Lindfield, Australia with this detailed map
- Explore Bonferraro, Italy with this detailed map
- Explore Doncaster, United Kingdom with this detailed map
