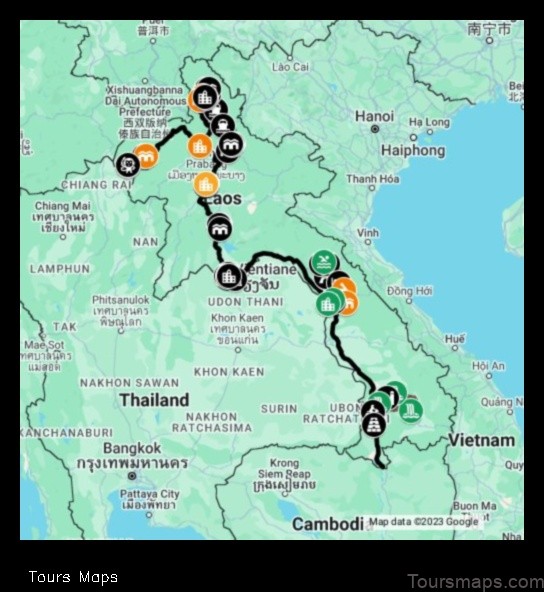
Map of Laos
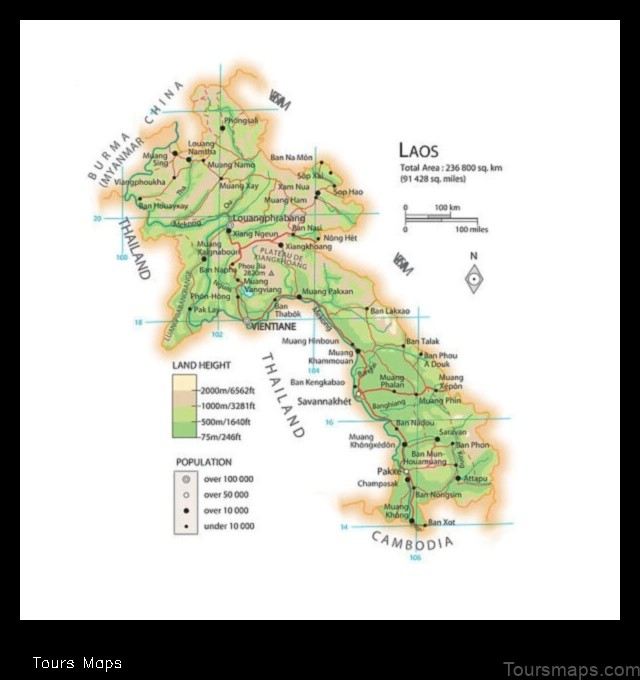
Laos is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar to the northwest, China to the northeast, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south, and Thailand to the west. Laos has a population of approximately 7 million people and a land area of 236,800 square kilometers. The capital of Laos is Vientiane.
The geography of Laos is diverse, with mountains, plateaus, and valleys. The Annamite Mountains run through the western part of the country, and the Mekong River flows through the eastern part. The climate of Laos is tropical, with hot, humid summers and mild winters.
The culture of Laos is influenced by its many ethnic groups, including the Lao, Hmong, Mien, Khmu, and Tai. The official language of Laos is Lao, but many people also speak other languages, such as Hmong, Mien, and Khmu. The religion of Laos is predominantly Theravada Buddhism, but there are also significant minorities of Christians and Muslims.
The economy of Laos is based on agriculture, mining, and tourism. The main agricultural products of Laos are rice, corn, sugarcane, and coffee. The main minerals of Laos are copper, gold, and silver. The main tourist destinations in Laos are the capital of Vientiane, the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Luang Prabang, and the Mekong River.
| Topic | Answer |
|---|---|
| Map of Laos | |
| Geography of Laos | Laos is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar to the northwest, China to the northeast, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south, and Thailand to the west. Laos has a total area of 236,800 square kilometers (91,400 sq mi), making it the 69th largest country in the world. The country is divided into 17 provinces and 1 municipality. |
| Provinces of Laos | The provinces of Laos are: |
| Cities of Laos | The largest cities in Laos are: |
| Travel features of Laos | Laos is a popular tourist destination due to its natural beauty, cultural heritage, and friendly people. Some of the most popular tourist destinations in Laos include: |
II. History of Laos
The history of Laos can be traced back to the 14th century, when the country was ruled by the Lan Xang Kingdom. The kingdom was divided into three parts in the 18th century, and Laos was eventually colonized by France in the 19th century. Laos gained independence from France in 1953, but was embroiled in a civil war from 1954 to 1975. The communist Pathet Lao won the civil war and established the Lao People’s Democratic Republic in 1975.
III. Geography of Laos
Laos is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar to the northwest, China to the northeast, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south, and Thailand to the west. Laos has a total area of 236,800 square kilometers (91,400 sq mi), making it the 69th largest country in the world. The country’s terrain is mostly mountainous, with the highest point being Mount Phou Bia at 2,817 meters (9,239 ft). The Mekong River flows through Laos from north to south, and is the country’s main transportation artery. Laos has a tropical climate, with warm, humid summers and cool, dry winters. The average annual temperature is 27 degrees Celsius (80 degrees Fahrenheit).
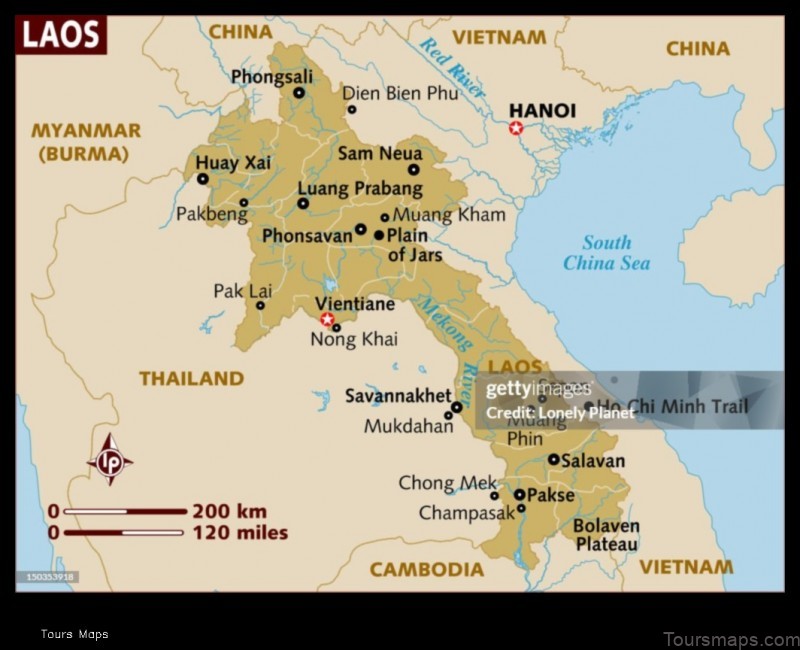
IV. Climate of Laos
The climate of Laos is tropical, with a hot, rainy season from May to October and a cooler, drier season from November to April. The average temperature in Vientiane, the capital, ranges from 22°C (72°F) in January to 32°C (90°F) in April. The average annual rainfall is around 1,800 mm (71 in).
The climate varies somewhat from region to region. The northern provinces are cooler and drier than the southern provinces, and the mountainous regions are cooler and more humid than the lowlands.
The rainy season is characterized by heavy rainfall, thunderstorms, and flooding. The dry season is characterized by clear skies, warm weather, and low humidity.
The climate of Laos can be a challenge for visitors, but it is also one of the country’s charms. The lush vegetation and abundant wildlife that thrive in the warm, humid climate are a major draw for tourists.
V. Culture of Laos
The culture of Laos is a blend of traditional Laotian and Buddhist beliefs, as well as influences from the country’s neighbors, such as Thailand, Vietnam, and China. The Laotian people are known for their hospitality, their love of music and dance, and their appreciation for nature.
The traditional religion of Laos is Theravada Buddhism, which is practiced by the majority of the population. Buddhism has had a profound influence on Laotian culture, and it is reflected in the country’s art, architecture, and music.
The Laotian people are also known for their love of music and dance. Traditional Laotian music is often played on traditional instruments, such as the khene (a bamboo mouth organ) and the pi (a reed pipe). Laotian dance is often performed at festivals and ceremonies, and it is characterized by its graceful movements and intricate steps.
The Laotian people also have a deep appreciation for nature. The country is home to a variety of beautiful natural landscapes, including mountains, forests, and rivers. The Laotian people often take time to enjoy the natural beauty of their country, and they believe that it is important to live in harmony with nature.
VI. Economy of Laos
The economy of Laos is a developing one, with a GDP of $18.6 billion in 2017. The country’s main economic activities are agriculture, mining, and tourism.
Agriculture accounts for about 30% of GDP and employs about 60% of the workforce. The main crops grown in Laos are rice, corn, sugarcane, and coffee.
Mining is another important economic activity in Laos. The country has significant reserves of copper, gold, and other minerals.
Tourism is a growing sector of the Lao economy. The country has a number of natural and cultural attractions, including the Mekong River, the Plain of Jars, and the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Luang Prabang.
The Lao government is working to diversify the economy and reduce its dependence on natural resources. The government is also working to improve the country’s infrastructure and attract foreign investment.
Despite the challenges, the Lao economy is growing and the country is making progress in its development.
Government of Laos
The government of Laos is a unitary state with a socialist political system. The head of state is the President, who is elected by the National Assembly for a five-year term. The Prime Minister is the head of government and is appointed by the President. The National Assembly is the unicameral legislature of Laos and is composed of 149 members who are elected for five-year terms.
The government of Laos is divided into three branches: the executive, the legislative, and the judicial. The executive branch is headed by the President, who is assisted by the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers. The legislative branch is the National Assembly, which is composed of 149 members who are elected for five-year terms. The judicial branch is headed by the Supreme People’s Court.
The government of Laos is a member of the United Nations, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), and the World Trade Organization (WTO).
Foreign relations of Laos
Laos’s foreign policy is based on the principles of independence, sovereignty, neutrality, non-alignment, and peaceful coexistence. The country pursues a policy of good neighborliness and friendly relations with all countries, regardless of their political and economic systems. Laos is a member of the United Nations, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM).
Laos’s relations with its neighbors are generally good. The country has signed a number of bilateral agreements with Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia, and Myanmar. Laos also has good relations with China, India, Japan, and the United States.
Laos’s relations with the United States have improved significantly in recent years. In 2016, the two countries signed a comprehensive partnership agreement that covers trade, investment, security, and development cooperation.
Laos’s relations with China are also strong. China is Laos’s largest trading partner and investor. The two countries have signed a number of agreements on economic cooperation, including a free trade agreement that came into effect in 2010.
Laos’s relations with Vietnam are close. The two countries share a long history and a common border. Vietnam is Laos’s second-largest trading partner and investor.
Laos’s relations with Cambodia are also good. The two countries share a border and have a long history of cooperation.
Laos’s relations with Myanmar are improving. The two countries have signed a number of agreements on trade and investment.
Laos’s relations with the international community are generally good. The country is a member of a number of international organizations, including the United Nations, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM).
Laos is a recipient of foreign aid from a number of countries, including China, Japan, the United States, and the European Union.
IX. Transportation in Laos
Laos has a well-developed transportation network, with roads, railways, and airports connecting major cities and towns. The country’s road network is extensive, and it is the primary means of transportation for both people and goods. The railway network is less extensive, but it does connect the major cities of Vientiane, Luang Prabang, and Pakse. Laos also has several international airports, the largest of which is Wattay International Airport in Vientiane.
The following is a brief overview of the transportation options available in Laos:
- Roads: Laos has a total of 37,843 kilometers of roads, of which 12,200 kilometers are paved. The main roads are well-maintained, but some of the secondary roads can be rough and difficult to travel.
- Railways: Laos has a total of 447 kilometers of railways, which connect the major cities of Vientiane, Luang Prabang, and Pakse. The railways are operated by the Lao State Railway.
- Airports: Laos has 11 international airports, the largest of which is Wattay International Airport in Vientiane. Other major airports include Luang Prabang International Airport and Pakse International Airport.
- Rivers: Laos has a number of navigable rivers, which are used for both transportation and trade. The Mekong River is the largest river in Laos, and it is used to transport goods between Thailand and Vietnam.
For more information on transportation in Laos, please visit the following websites:
FAQ
Here are three common questions about Laos and their answers:
Q: What is the capital of Laos?
A: The capital of Laos is Vientiane.
Q: What are the major cities in Laos?
A: The major cities in Laos include Vientiane, Luang Prabang, Savannakhet, and Pakse.
Q: What is the official language of Laos?
A: The official language of Laos is Lao.
Table of Contents
Maybe You Like Them Too
- Explore Doncaster, United Kingdom with this detailed map
- Explore Arroyito, Argentina with this Detailed Map
- Explore Belin, Romania with this detailed map
- Explore Almudévar, Spain with this detailed map
- Explore Aguarón, Spain with this detailed map
