I. Introduction
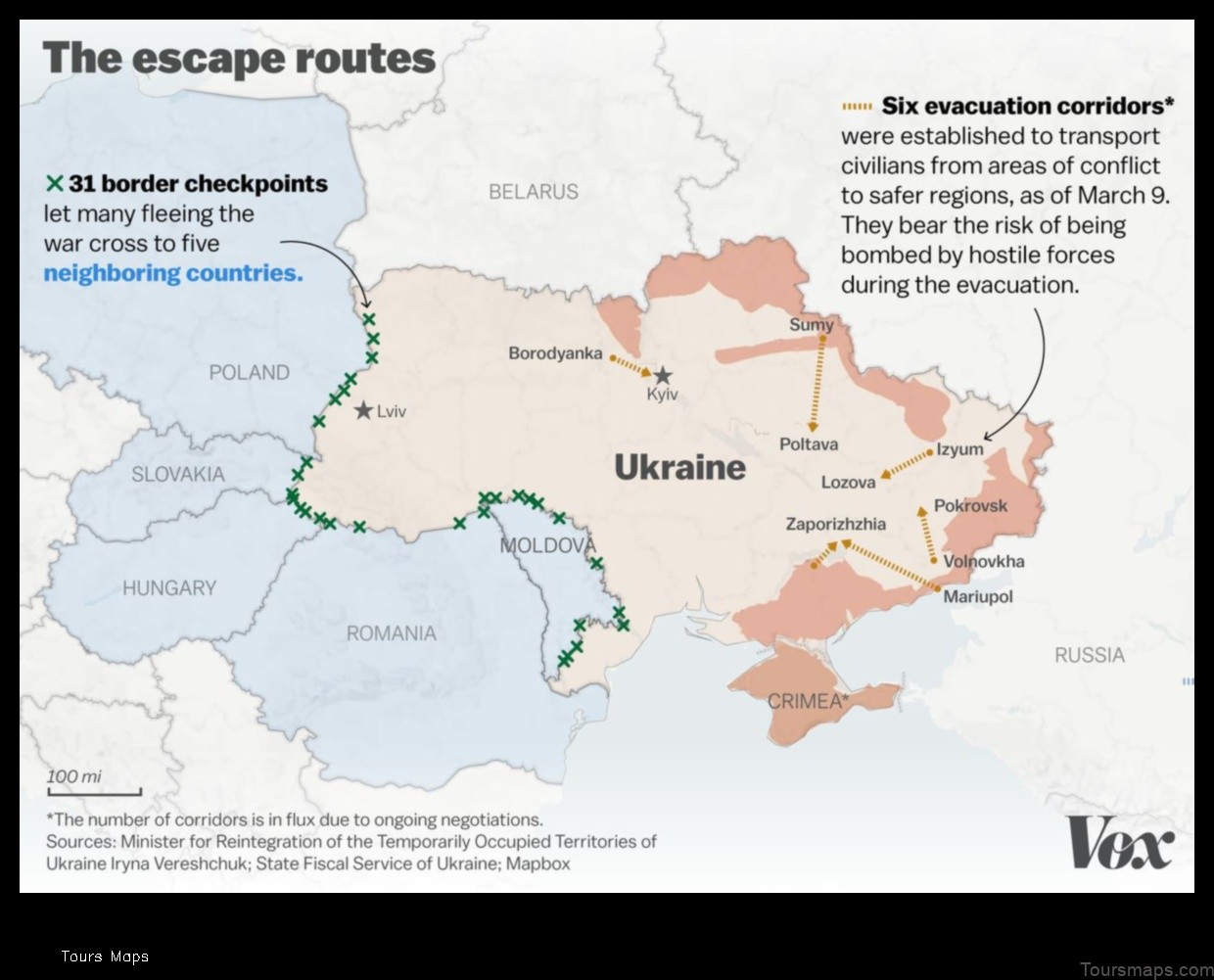
Ukraine is a country located in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east, Belarus to the north, Poland to the west, Slovakia and Hungary to the southwest, and Romania and Moldova to the south. Ukraine has a population of over 44 million people and is the second-largest country in Europe by area.
II. History of Ukraine
The history of Ukraine dates back to the Neolithic period. The first major civilization in Ukraine was the Scythians, who ruled the region from the 7th century BC to the 2nd century AD. The Scythians were followed by the Sarmatians, who ruled from the 2nd century BC to the 4th century AD. In the 4th century AD, the Huns invaded Ukraine and conquered the Sarmatians. The Huns were followed by the Goths, who ruled from the 4th century AD to the 6th century AD.
The Kievan Rus
In the 9th century AD, the Slavic tribes of Ukraine united under the leadership of Prince Rurik and formed the Kievan Rus. The Kievan Rus was a powerful state that controlled much of Eastern Europe. The Kievan Rus was also a center of culture and learning. In the 12th century AD, the Kievan Rus was invaded by the Mongols and fell into decline.
The Cossacks
In the 15th century AD, the Cossacks emerged in Ukraine. The Cossacks were a group of independent warriors who lived on the steppes of Ukraine. The Cossacks fought against the Mongols and the Poles. In the 17th century AD, the Cossacks established the Zaporozhian Sich, a Cossack republic on the Dnieper River.
The Russian Empire
In the 18th century AD, the Russian Empire annexed Ukraine. Ukraine was part of the Russian Empire until the Russian Revolution in 1917.
The Ukrainian People’s Republic
In the aftermath of the Russian Revolution, the Ukrainian People’s Republic was proclaimed in 1917. The Ukrainian People’s Republic was a short-lived state that was eventually conquered by the Soviet Union.
The Soviet Union
Ukraine was part of the Soviet Union from 1922 to 1991. During the Soviet era, Ukraine was a major industrial and agricultural center.
The Independent Ukraine
In 1991, Ukraine declared its independence from the Soviet Union. Ukraine is now a sovereign state and a member of the United Nations.
III. Geography of Ukraine
Ukraine is located in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east, Belarus to the north, Poland to the west, Slovakia and Hungary to the southwest, and Romania and Moldova to the south. Ukraine has a total area of 603,628 square kilometers (233,062 square miles).
Ukraine is a landlocked country. The highest point in Ukraine is Mount Hoverla, which is 2,061 meters (6,762 feet) high. The lowest point in Ukraine is the Black Sea, which is 0 meters (0 feet) above sea level.
Ukraine has a temperate climate. The winters are cold and snowy, and the summers are warm and humid.
IV. Population of Ukraine
The population of Ukraine is over 44 million people. The majority of the population is Ukrainian, but there are also large minorities of Russians, Belarusians, and Moldovans.
The population of Ukraine is concentrated in the eastern and central parts of the country. The largest cities in Ukraine are Kyiv, Kharkiv, and Lviv.
V. Economy of Ukraine
The economy of Ukraine is a mixed economy. The service sector is the largest sector of the economy, followed by the industrial sector and the agricultural sector.
Ukraine is a major producer of agricultural products, such as wheat, corn, and sunflower seeds. Ukraine is also a major producer of metals, such as iron and steel.
| Topic | Feature |
|---|---|
| Ukraine map | A comprehensive map of Ukraine, including its geography, history, and culture. |
| Ukraine travel | Information on how to travel to Ukraine, including visas, transportation, and accommodation. |
| Eastern Europe | A guide to Eastern Europe, including its history, culture, and tourism. |
| Ukraine culture | A look at the culture of Ukraine, including its music, art, and cuisine. |
| Ukraine history | A history of Ukraine, from its early beginnings to the present day. |
I. Introduction
Ukraine is a country located in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Belarus to the north, Poland to the west, Slovakia and Hungary to the southwest, Romania and Moldova to the south, and Russia to the east. Ukraine has a population of over 44 million people and is the second-largest country in Europe by area.
III. Geography of Ukraine
Ukraine is located in Eastern Europe, and borders Belarus to the north, Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary to the west, Romania and Moldova to the south, and Russia to the east. The country has a total area of 603,628 square kilometers (233,062 sq mi), making it the second-largest country in Europe after Russia. Ukraine’s landscape is diverse, with plains, mountains, and forests. The Carpathian Mountains are located in the west of the country, and the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov are located to the south.
II. History of Ukraine
The history of Ukraine is a long and complex one, dating back to the early days of human civilization. The region has been inhabited by a variety of different cultures and peoples over the centuries, and has been ruled by a number of different empires and states.
The first known inhabitants of Ukraine were the Trypillian culture, who lived in the region from around 5000 to 2750 BC. The Trypillian culture was followed by the Scythians, who ruled the region from around 700 to 200 BC. The Scythians were then conquered by the Sarmatians, who ruled the region from around 200 BC to AD 450.
In the 5th century AD, the Slavic peoples began to migrate to Ukraine. The Slavic peoples were eventually united under the rule of the Kievan Rus, which was founded in the 9th century AD. The Kievan Rus was a powerful state that reached its peak in the 11th century AD. However, the Kievan Rus began to decline in the 12th century AD, and was eventually destroyed by the Mongols in the 13th century AD.
After the collapse of the Kievan Rus, Ukraine was divided into a number of different principalities. These principalities were eventually conquered by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the 14th century AD. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was then conquered by the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in the 16th century AD.
In the 18th century AD, Ukraine was divided between the Russian Empire and the Habsburg Monarchy. The Russian Empire annexed most of Ukraine in the 18th century AD, while the Habsburg Monarchy annexed Galicia and Bukovina in the 18th and 19th centuries AD.
In the 20th century AD, Ukraine was ruled by the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union, and the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic was one of the founding republics of the Soviet Union in 1922. Ukraine declared its independence from the Soviet Union in 1991.
V. Economy of Ukraine
The economy of Ukraine is a developing economy with a GDP of $155.7 billion (nominal, 2023 est.). The country’s economy is based on a variety of sectors, including agriculture, manufacturing, and services. Ukraine is a major exporter of agricultural products, including wheat, corn, and sunflower oil. The country also has a significant manufacturing sector, which produces a variety of goods, including machinery, chemicals, and metals. Ukraine’s services sector is also growing rapidly, and includes a number of financial services, telecommunications, and tourism businesses.
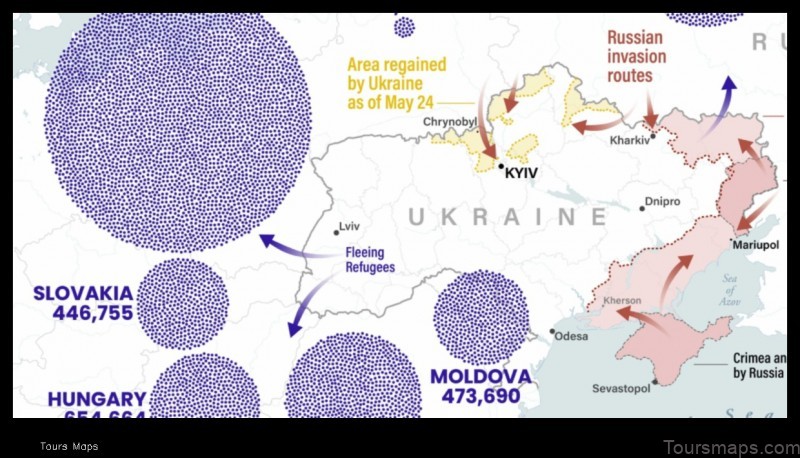
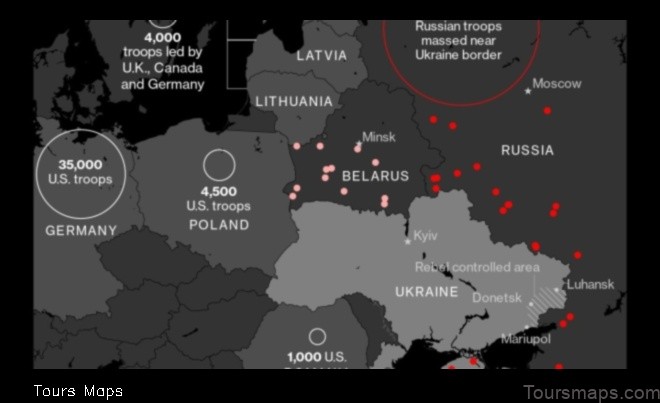
The Ukrainian economy has been negatively affected by the ongoing Russian invasion. The invasion has caused a significant disruption to the country’s economy, leading to a decline in output and investment. The war has also caused a sharp increase in inflation, and has made it difficult for businesses to operate.
Despite the challenges posed by the war, the Ukrainian economy is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. The country has a young and educated population, and a strong industrial base. Ukraine is also located in a strategic location, and has a number of trade agreements with other countries.
The Ukrainian government is working to rebuild the country’s economy after the war. The government is providing financial assistance to businesses, and is working to attract foreign investment. The government is also working to improve the country’s infrastructure, and to make it easier for businesses to operate.
The Ukrainian economy is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. However, the country will need to address a number of challenges in order to achieve sustainable long-term growth. These challenges include the need to improve the country’s infrastructure, to attract foreign investment, and to reduce corruption.
VI. Government of Ukraine
The government of Ukraine is a unitary, semi-presidential republic. The President of Ukraine is the head of state and the Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces. The Prime Minister of Ukraine is the head of government and is appointed by the President with the approval of the Verkhovna Rada (Ukrainian Parliament). The Verkhovna Rada is the unicameral legislature of Ukraine and is composed of 450 deputies.
The government of Ukraine is responsible for the formulation and implementation of domestic and foreign policy, the administration of the state apparatus, and the maintenance of law and order. The government is also responsible for the provision of public services, such as education, healthcare, and social security.
The government of Ukraine is a complex and evolving institution. It is constantly being reformed in order to improve its efficiency and effectiveness. The government is also facing a number of challenges, including corruption, economic inequality, and regional instability.
Despite these challenges, the government of Ukraine is committed to building a democratic and prosperous country. The government is working to improve the rule of law, strengthen the economy, and promote social justice. The government is also working to resolve the conflict in eastern Ukraine and to integrate the country into the European Union and NATO.
VII. Culture of Ukraine
The culture of Ukraine is a diverse and rich one, influenced by its history and location. It is a blend of Slavic, Turkic, and other influences, and has been shaped by centuries of interaction with its neighbors.
The Ukrainian language is the official language of Ukraine, and is spoken by the majority of the population. It is a Slavic language, and is closely related to Russian and Belarusian. There are also a number of other minority languages spoken in Ukraine, including Russian, Romanian, Hungarian, and Tatar.
The traditional religion of Ukraine is Eastern Orthodoxy, and the majority of the population is Orthodox Christian. However, there are also a significant number of Protestants, Catholics, and Muslims in Ukraine.
Ukrainian culture is known for its vibrant folk art, music, and dance. The traditional dress of Ukraine is also very distinctive, and is often embroidered with colorful designs.
Ukrainian cuisine is also very popular, and is known for its hearty soups, stews, and dumplings. The national dish of Ukraine is borscht, a hearty soup made with beets, cabbage, and meat.
Ukraine is a beautiful country with a rich culture and history. It is a popular tourist destination, and visitors can enjoy its many historical sites, museums, and cultural events.
VIII. Religion in Ukraine
The most common religion in Ukraine is Eastern Orthodox Christianity, which is practiced by about 70% of the population. Other religious groups include Roman Catholics, Protestants, Jews, and Muslims.
The Ukrainian Orthodox Church is divided into two main branches: the Ukrainian Orthodox Church–Moscow Patriarchate and the Ukrainian Orthodox Church–Kyiv Patriarchate. The Ukrainian Orthodox Church–Moscow Patriarchate is the larger of the two branches and is under the jurisdiction of the Russian Orthodox Church. The Ukrainian Orthodox Church–Kyiv Patriarchate is the smaller of the two branches and is independent of the Russian Orthodox Church.
Roman Catholicism is the second largest religion in Ukraine, with about 10% of the population identifying as Roman Catholic. The majority of Roman Catholics in Ukraine are ethnic Ukrainians, but there are also significant numbers of Polish and Hungarian Roman Catholics.
Protestantism is the third largest religion in Ukraine, with about 5% of the population identifying as Protestant. The most common Protestant denominations in Ukraine are Baptists, Lutherans, and Pentecostals.
Jews make up about 1% of the population of Ukraine. The majority of Jews in Ukraine are Ashkenazi Jews, but there are also significant numbers of Sephardic Jews and Karaites.
Muslims make up about 1% of the population of Ukraine. The majority of Muslims in Ukraine are ethnic Tatars, but there are also significant numbers of ethnic Ukrainians and other ethnic groups who practice Islam.
The constitution of Ukraine guarantees freedom of religion and the government generally respects this right. However, there have been some reports of discrimination against religious minorities, particularly Jehovah’s Witnesses and Pentecostals.
IX. Religion in Ukraine
Religion in Ukraine is diverse, with the majority of the population identifying as Eastern Orthodox Christians. Other religious groups include Roman Catholics, Protestants, Muslims, Jews, and Hindus. The Ukrainian Orthodox Church is the largest religious denomination in the country, with over 30 million members. The Ukrainian Catholic Church is the second largest religious denomination, with over 5 million members. Other religious groups include the Lutheran Church, the Baptist Church, the Pentecostal Church, and the Methodist Church.
The Ukrainian Constitution guarantees freedom of religion, and the government generally respects this right in practice. However, there have been some reports of discrimination against religious minorities, particularly Jehovah’s Witnesses and Muslims.
The Ukrainian government has a policy of neutrality towards religion, and it does not provide financial support to any religious group. However, the government does provide funding for religious education in public schools.
Religion plays an important role in the lives of many Ukrainians. Churches and other religious institutions are often involved in social welfare activities, such as providing food and shelter to the poor. Religion is also a source of comfort and support for many Ukrainians during times of crisis.
X. FAQ
Q: What is the capital of Ukraine?
A: The capital of Ukraine is Kyiv.
Q: What is the population of Ukraine?
A: The population of Ukraine is approximately 44 million people.
Q: What is the official language of Ukraine?
A: The official language of Ukraine is Ukrainian.
Table of Contents
Maybe You Like Them Too
- Explore Doncaster, United Kingdom with this detailed map
- Explore Arroyito, Argentina with this Detailed Map
- Explore Belin, Romania with this detailed map
- Explore Almudévar, Spain with this detailed map
- Explore Aguarón, Spain with this detailed map
