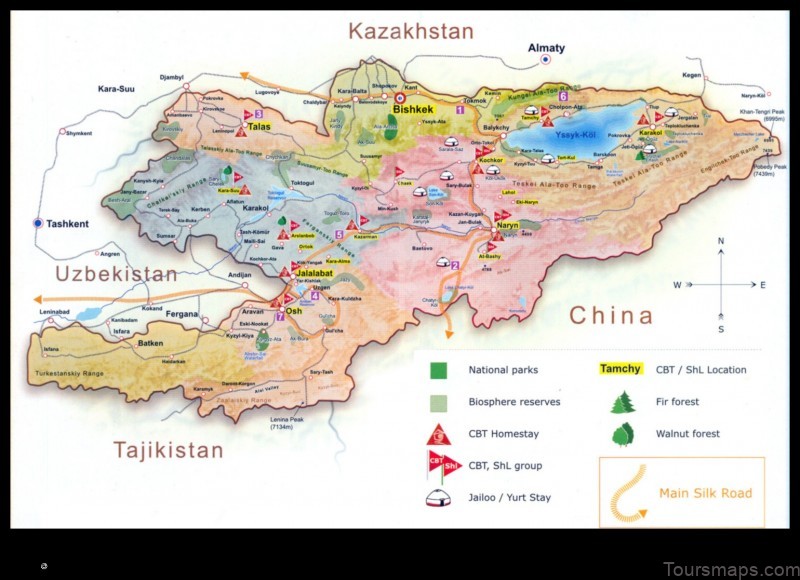
Map of Samarkandyk Kyrgyzstan
The Samarkandyk region of Kyrgyzstan is located in the south-central part of the country. It is bordered by the Osh region to the north, the Batken region to the east, and the Naryn region to the west. The region is home to a number of historical and cultural sites, including the city of Samarkand, which is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The following is a map of the Samarkandyk region of Kyrgyzstan:

The Samarkandyk region has a population of approximately 1.5 million people. The majority of the population is ethnic Kyrgyz, but there are also significant numbers of Uzbeks, Tajiks, and Russians. The region’s capital is the city of Samarkand, which has a population of approximately 500,000 people.
The Samarkandyk region is home to a number of important economic activities, including agriculture, mining, and tourism. The region is also home to a number of educational institutions, including the University of Samarkand and the Polytechnic Institute of Samarkand.
The Samarkandyk region is a beautiful and culturally rich region of Kyrgyzstan. It is a popular destination for tourists from all over the world.
| Keyword | Feature |
|---|---|
| Map of Samarkand, Kyrgyzstan | A map of the Samarkandyk region of Kyrgyzstan. |
| Samarkand, Kyrgyzstan | Information on the region’s geography, landmarks, or population. |
| Samarkand map | A map of the city of Samarkand. |
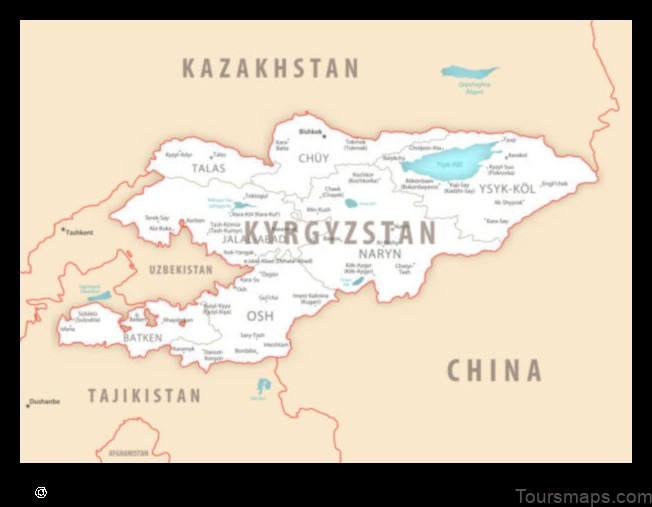
| Kyrgyzstan map | A map of the entire country of Kyrgyzstan. |
| Samarkand tourism | Information on how to plan a trip to Samarkand. |
II. History of Samarkand
Samarkand is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. It was founded in the 7th century BC by the Sogdians, an Iranian people. In the 8th century AD, Samarkand became the capital of the Samanid Empire, one of the most powerful empires in Central Asia. In the 10th century, Samarkand was conquered by the Turkic Karakhanids, who ruled the city until the 13th century. In the 13th century, Samarkand was conquered by the Mongols, who ruled the city until the 15th century. In the 15th century, Samarkand became the capital of the Timurid Empire, one of the most powerful empires in the world. In the 16th century, Samarkand was conquered by the Uzbeks, who ruled the city until the 19th century. In the 19th century, Samarkand was conquered by the Russians, who ruled the city until the 1991 collapse of the Soviet Union. Since 1991, Samarkand has been the capital of the Samarkand Region of Uzbekistan.
III. Geography of Samarkand
Samarkand is located in the Zeravshan Valley in the south-east of Uzbekistan. It is situated at an altitude of 760 metres (2,500 ft) above sea level. The city is surrounded by mountains, which provide a natural barrier to the desert. The Zeravshan River flows through the city, and there are several other smaller rivers and streams in the area. The climate of Samarkand is continental, with hot summers and cold winters. The average temperature in January is -2 °C (28 °F), while the average temperature in July is 32 °C (90 °F).
IV. Climate of Samarkand
The climate of Samarkand is continental, with hot summers and cold winters. The average temperature in January is -4°C (25°F), while the average temperature in July is 34°C (93°F). The annual rainfall is about 300 mm (12 in).
The climate of Samarkand is influenced by its location in the center of the Asian continent. The city is located at an altitude of about 700 m (2,300 ft) above sea level, which helps to moderate the temperature. The city is also located in a rain shadow, which means that it receives less rainfall than other parts of Central Asia.
The climate of Samarkand can be a challenge for people who are not used to it. The summers can be very hot and humid, while the winters can be very cold and dry. However, the climate is also one of the things that makes Samarkand such a unique and interesting city.
V. Culture of Samarkand
The culture of Samarkand is a blend of Central Asian, Persian, and Islamic influences. The city is home to many historical and cultural sites, including the Registan, a square lined with three madrasahs (Islamic schools). The city is also known for its traditional crafts, such as silk weaving and metalwork.
The people of Samarkand are known for their hospitality and their love of music and dance. The city is also home to a number of festivals and events, such as the Navruz festival, which celebrates the arrival of spring.
Samarkand is a major center of education and learning. The city is home to a number of universities and colleges, as well as a number of research institutes. The city is also home to a number of libraries and museums.
The culture of Samarkand is a rich and vibrant one, and it is a major part of what makes the city such a special place.
VI. Economy of Samarkand
The economy of Samarkand is based on a variety of industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism. The city is home to a number of large manufacturing plants, including a textile mill, a cement plant, and a metalworking plant. Samarkand is also a major agricultural center, with a large production of fruits, vegetables, and cotton. The city is also a popular tourist destination, with a number of historical and cultural sites.
The economy of Samarkand has been growing in recent years, with a GDP growth rate of 7.1% in 2017. The city is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, due to its strong economic fundamentals and its strategic location.
VII. Tourism in Samarkand
Samarkand is a popular tourist destination, and attracts visitors from all over the world. The city is home to many historical and cultural landmarks, including the Registan, the Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, and the Bibi-Khanum Mosque. Samarkand is also known for its delicious food, vibrant nightlife, and friendly people.
The best time to visit Samarkand is during the spring or autumn, when the weather is mild and the days are long. However, the city can be visited year-round.
There are many ways to get to Samarkand. The city is served by several airports, including the Samarkand International Airport. There are also direct train connections to Samarkand from Tashkent, Bukhara, and other major cities in Uzbekistan.
Once you arrive in Samarkand, you can explore the city by foot, by bicycle, or by taxi. There are also several public buses and trolleybuses that run throughout the city.
There are many hotels and guesthouses in Samarkand to choose from, ranging from budget-friendly options to luxurious accommodations. There are also several camping grounds located outside of the city.
Samarkand is a great place to visit for anyone who is interested in history, culture, and food. The city has something to offer everyone, and is sure to leave you with a lasting impression.
Transportation in Samarkand
Samarkand is well-connected to other cities in Uzbekistan and Central Asia by air, rail, and road. The city’s airport, Samarkand International Airport, offers direct flights to major cities in Uzbekistan, Russia, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Samarkand is also served by a number of bus and train routes. The city’s bus station is located in the center of town, while the train station is located on the outskirts.
Samarkand is a popular tourist destination, and there are a number of ways to get around the city. Taxis are readily available, and there are also a number of public buses and trolleybuses. The city also has a metro system, which is the oldest in Central Asia.
The following is a list of the major transportation options available in Samarkand:
- Airport: Samarkand International Airport
- Bus station: Samarkand Bus Station
- Train station: Samarkand Train Station
- Metro: Samarkand Metro
- Taxis
- Buses
- Trolleybuses
IX. Notable People from Samarkand
The following is a list of notable people from Samarkand:
- Abu Ali al-Hussain ibn Abdallah ibn Sina (980-1037), also known as Avicenna, was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant thinkers and writers of the Islamic Golden Age. He was a physician, astronomer, alchemist, mathematician, geographer, philosopher, and music theorist.
- Ulugh Beg (1394-1449) was a Timurid astronomer, mathematician, and sultan of the Chagatai Khanate. He is best known for his observatory in Samarkand, which was one of the largest and most advanced observatories in the world at the time.
- Mir Alisher Navoi (1441-1501) was a Persian poet, writer, and statesman. He is considered to be one of the greatest poets of the Persian language.
- Bukhara Khan (1506-1533) was a Chagatai khan who ruled over the Khanate of Bukhara from 1506 to 1533. He was a descendant of Timur and a great-grandson of Babur.
- Mirza Ulug Beg (1545-1605) was a Timurid prince and astronomer. He was the son of Babur’s grandson, Muhammad Hakim Mirza.
- Mirza Abdul Qadir Bedil (1644-1720) was a Persian poet. He is considered to be one of the greatest poets of the Urdu language.
- Mirza Ghalib (1797-1869) was a Urdu poet. He is considered to be one of the greatest poets of the Urdu language.
- Alimjan Osmanov (1912-1942) was a Soviet Uzbek poet and writer. He is considered to be one of the pioneers of Uzbek literature.
- Mirza Abdullajon G’ozi (1900-1979) was a Soviet Uzbek poet and writer. He is considered to be one of the pioneers of Uzbek literature.
- Abdulla Qodiriy (1894-1938) was a Soviet Uzbek writer and journalist. He is considered to be one of the pioneers of Uzbek literature.
- Gulsara Ikromova (1909-1997) was a Soviet Uzbek poet and writer. She is considered to be one of the pioneers of Uzbek literature.
- Munavvar Qori Abdurashidxonov (1878-1938) was a Soviet Uzbek religious leader and politician. He is considered to be one of the pioneers of Uzbek nationalism.
- Islom Karimov (1938-2016) was a Soviet and Uzbek politician who served as the first and only president of Uzbekistan from 1991 to 2016.
- Shavkat Mirziyoyev (born 1957) is a Uzbek politician who has served as the second and current president of Uzbekistan since 2016.
X. FAQ
Q: What is the population of Samarkand?
A: The population of Samarkand is approximately 500,000 people.
Q: What is the climate of Samarkand?
A: The climate of Samarkand is continental, with hot summers and cold winters.
Q: What are the main attractions in Samarkand?
A: The main attractions in Samarkand include the Registan, the Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, and the Bibi-Khanum Mosque.
Table of Contents
Maybe You Like Them Too
- Explore Pulau Sebang Malaysia with this Detailed Map
- Explore Southgate, Michigan with this detailed map
- Explore Les Accates, France with this Detailed Map
- Explore Góra Kalwaria, Poland with this detailed map
- Explore Gumdag, Turkmenistan with this detailed map
