Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is a French overseas department and region in the Caribbean Sea. It is composed of two main islands, Guadeloupe and La Désirade, as well as several smaller islands. Guadeloupe has a population of about 400,000 people and a land area of about 1,628 square kilometers. The capital of Guadeloupe is Basse-Terre.
Guadeloupe is a popular tourist destination due to its beautiful beaches, lush rainforests, and diverse wildlife. The island is also home to a number of historical and cultural sites, including the Fort Louis de Fort-de-France, the Cathedral of Saint-Pierre-et-Saint-Paul, and the La Soufrière volcano.
The climate in Guadeloupe is tropical, with warm weather year-round. The average temperature ranges from 25°C to 30°C. The rainy season runs from June to November, and the dry season runs from December to May.
The economy of Guadeloupe is based on tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing. The main agricultural products grown in Guadeloupe include bananas, sugar cane, and coffee. The main manufactured goods produced in Guadeloupe include rum, processed foods, and electronics.
The government of Guadeloupe is a parliamentary democracy. The head of state is the President of France, and the head of government is the President of the Regional Council of Guadeloupe.
The transportation system in Guadeloupe is well-developed. The island has a network of highways, as well as airports and seaports. The main airport in Guadeloupe is the Pointe-à-Pitre International Airport.
Tourism is a major industry in Guadeloupe. The island attracts tourists from all over the world who come to enjoy its beautiful beaches, lush rainforests, and diverse wildlife. The main tourist destinations in Guadeloupe include the beaches of Sainte-Anne, the rainforests of Basse-Terre, and the volcano of La Soufrière.
Here are some frequently asked questions about Guadeloupe:
- What is the capital of Guadeloupe?
- What is the population of Guadeloupe?
- What is the climate in Guadeloupe?
- What is the economy of Guadeloupe?
- What is the government of Guadeloupe?
- What is the transportation system in Guadeloupe?
- What are the main tourist destinations in Guadeloupe?
| Topic | Feature |
|---|---|
| Guadeloupe Map | A map of the island of Guadeloupe |
| Guadeloupe Tourism | Information on tourism in Guadeloupe, including attractions, activities, and accommodations |
| Guadeloupe Travel | Information on how to get to Guadeloupe, including flights, ferries, and car rentals |
| Guadeloupe Geography | Information on the geography of Guadeloupe, including its climate, terrain, and wildlife |
| Guadeloupe Beaches | Information on the beaches of Guadeloupe, including their location, amenities, and activities |
II. History of Guadeloupe
The history of Guadeloupe can be traced back to the 15th century, when the island was first discovered by Europeans. The island was originally inhabited by the Carib people, but it was soon colonized by the French. Guadeloupe remained a French colony for over 300 years, and it was during this time that the island developed its unique culture and identity. In 1946, Guadeloupe became an overseas department of France, and it has maintained this status ever since.
III. Geography of Guadeloupe
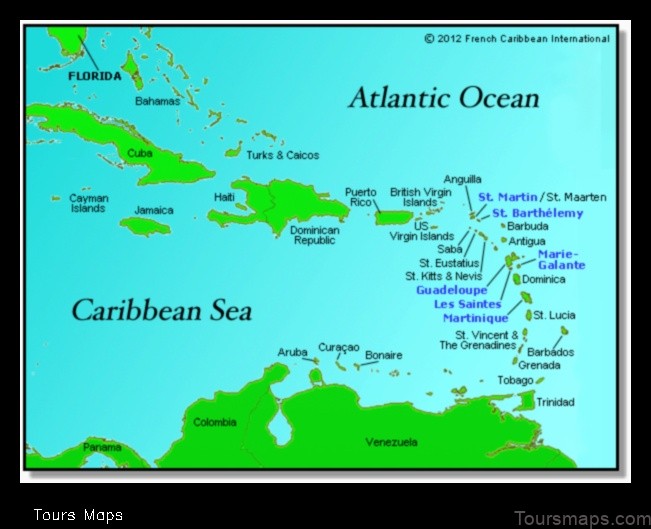
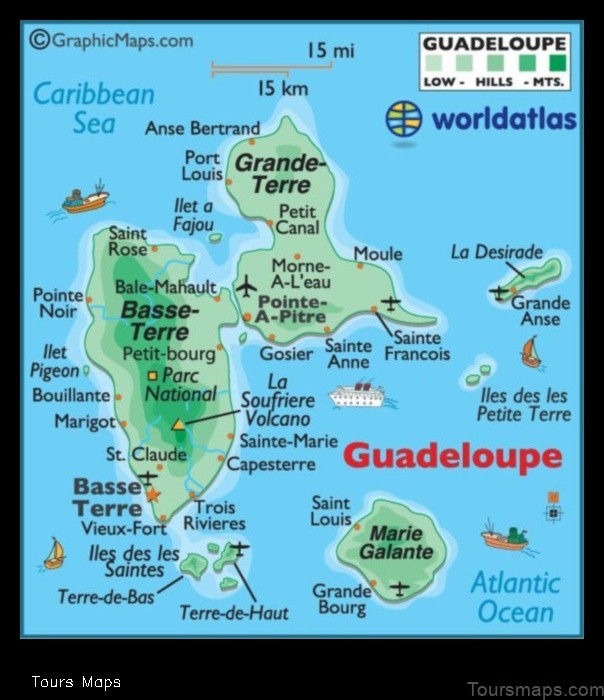
Guadeloupe is a French overseas department located in the Caribbean Sea. It consists of two main islands, Grande-Terre and Basse-Terre, as well as several smaller islands. The total land area of Guadeloupe is 1,628 square kilometers (629 square miles).
Grande-Terre is the larger of the two main islands, with a population of approximately 400,000 people. It is a flat, low-lying island with a coastline of approximately 250 kilometers (155 miles). The capital of Guadeloupe, Pointe-à-Pitre, is located on Grande-Terre.
Basse-Terre is the smaller of the two main islands, with a population of approximately 250,000 people. It is a mountainous island with a coastline of approximately 100 kilometers (62 miles). The highest point in Guadeloupe, Mount Soufrière, is located on Basse-Terre.
The climate of Guadeloupe is tropical, with average temperatures ranging from 25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F). The rainy season typically lasts from June to November, and the dry season lasts from December to May.
The vegetation of Guadeloupe is diverse, and includes rainforests, mangrove forests, and savannas. The island is home to a variety of animals, including birds, reptiles, amphibians, and mammals.
III. Geography of Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is a French overseas department and region in the Caribbean Sea. It is composed of two main islands, Grande-Terre and Basse-Terre, as well as several smaller islands. The total land area of Guadeloupe is 1,628 square kilometers (629 square miles).
Grande-Terre is the larger of the two main islands, with an area of 1,436 square kilometers (555 square miles). It is a flat, low-lying island with a coastline of about 250 kilometers (155 miles). The island is mostly covered in sugarcane fields and other agricultural land.
Basse-Terre is the smaller of the two main islands, with an area of 192 square kilometers (74 square miles). It is a mountainous island with a coastline of about 100 kilometers (62 miles). The island is home to the highest point in Guadeloupe, La Soufrière, which is an active volcano.
The climate of Guadeloupe is tropical, with average temperatures ranging from 25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F). The island receives an average of 1,500 millimeters (60 inches) of rainfall per year, with most of the rain falling during the hurricane season from June to November.
The vegetation of Guadeloupe is diverse, and includes rainforests, mangrove forests, and coral reefs. The island is home to a variety of animals, including birds, reptiles, and fish.
The population of Guadeloupe is about 400,000 people. The majority of the population is of African descent, with a significant minority of European and Creole descent. The official language of Guadeloupe is French, but Creole is also spoken by many people.
The economy of Guadeloupe is based on tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing. The island is a popular tourist destination, and attracts visitors from all over the world. The main agricultural products of Guadeloupe include sugarcane, bananas, and coffee. The island also has a number of manufacturing industries, including rum production, food processing, and electronics assembly.
Guadeloupe is a beautiful and diverse island with a rich culture and history. The island is a popular tourist destination, and offers a variety of activities for visitors to enjoy.
V. Culture of Guadeloupe
The culture of Guadeloupe is a blend of French, African, and Caribbean influences. The island’s cuisine, music, and dance are all influenced by these different cultures. Guadeloupean cuisine is known for its use of fresh seafood, tropical fruits, and spices. The island’s music is a mix of traditional French and African music, with a Caribbean influence. Guadeloupean dance is also a mix of traditional French and African dance, with a Caribbean influence.
The culture of Guadeloupe is a vibrant and diverse one, and it is a major part of what makes the island so unique.
VI. Economy of Guadeloupe
The economy of Guadeloupe is based on tourism, agriculture, and industry. The tourism industry is the largest contributor to the economy, accounting for over 25% of GDP. Guadeloupe is a popular tourist destination due to its beautiful beaches, lush rainforests, and historic cities. The agricultural sector is also important to the economy, with sugarcane being the main crop. Guadeloupe is also home to a number of industries, including the rum, perfume, and electronics industries. The economy of Guadeloupe is closely linked to the economy of France, and the euro is the official currency.
VII. Government of Guadeloupe
The government of Guadeloupe is a semi-autonomous collectivité territoriale of France. It is governed by a president, who is elected by the people of Guadeloupe, and a council of ministers, who are appointed by the president. The council of ministers is responsible for the day-to-day running of the government, while the president is responsible for representing Guadeloupe on the international stage.
Guadeloupe is divided into four administrative regions: Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Les Saintes, and Marie-Galante. Each region is governed by a regional council, which is elected by the people of the region. The regional councils are responsible for a variety of matters, including education, health care, and transportation.
The government of Guadeloupe is funded by a variety of sources, including taxes, government fees, and grants from the French government. The government’s budget is used to fund a variety of programs and services, including education, health care, and infrastructure development.
Transportation in Guadeloupe
Transportation in Guadeloupe is a vital part of the island’s economy and tourism industry. The island has a well-developed road network, and there are also several airports and seaports. The main airport is Pointe-à-Pitre International Airport, which is located on the island of Grande-Terre. There are also several smaller airports on the other islands of Guadeloupe. The main seaport is Pointe-à-Pitre Port, which is located on the island of Grande-Terre. There are also several smaller seaports on the other islands of Guadeloupe.
The most popular way to travel around Guadeloupe is by car. There are a number of rental car companies on the island, and it is easy to rent a car at the airport or at one of the major hotels. The roads in Guadeloupe are generally well-maintained, and it is easy to get around the island.
There are also a number of public transportation options available in Guadeloupe. The bus system is the most popular option, and there are buses that run to all of the major towns and cities on the island. There are also a number of taxis available, and they are a convenient way to get around the island.
Guadeloupe is also a popular destination for cruise ships, and there are a number of cruise ships that stop at the island each year. The cruise ships dock at Pointe-à-Pitre Port, and there are a number of tours and excursions available for cruise ship passengers.
IX. Tourism in Guadeloupe
Tourism is a major industry in Guadeloupe, and the island attracts over two million visitors each year. The most popular tourist destinations include the capital city of Basse-Terre, the beach resort of Saint-François, and the volcanic island of La Désirade. Guadeloupe offers a wide variety of tourist attractions, including beautiful beaches, lush rainforests, and historical sites. The island is also home to a number of cultural festivals and events, which attract visitors from all over the world.
The tourism industry in Guadeloupe is supported by a number of government agencies and organizations, including the Guadeloupe Tourism Board and the Guadeloupe Chamber of Commerce. These organizations work to promote the island to potential visitors and to provide them with information about the island’s attractions and amenities.
Tourism is a major contributor to the Guadeloupean economy, and it is estimated that the industry generates over €1 billion in revenue each year. The tourism industry also provides employment for a large number of people in Guadeloupe.
Despite the economic benefits of tourism, the industry has also had some negative impacts on Guadeloupe. For example, tourism has led to increased development in some areas of the island, which has put pressure on the environment. Tourism has also contributed to the rise in crime rates in some areas of Guadeloupe.
Despite these challenges, tourism remains a major industry in Guadeloupe and it is expected to continue to grow in the years to come.
X. FAQ
Q: What is the capital of Guadeloupe?
A: The capital of Guadeloupe is Basse-Terre.
Q: What is the population of Guadeloupe?
A: The population of Guadeloupe is approximately 400,000 people.
Q: What is the official language of Guadeloupe?
A: The official language of Guadeloupe is French.
Table of Contents
Maybe You Like Them Too
- Explore Bonferraro, Italy with this detailed map
- Explore Doncaster, United Kingdom with this detailed map
- Explore Arroyito, Argentina with this Detailed Map
- Explore Belin, Romania with this detailed map
- Explore Almudévar, Spain with this detailed map
