Jacques Nicolas Gobert in Honduras
The Gobert tomb is topped with a statue of Major General Jacques Nicolas Gobert depicting the moment he was shot in the head during the Battle of Bailen (a small town in southern Spain about 100 miles east of Cordova). The Battle of Bailen proved to be one of Napoleon’s worst defeats of the Peninsular War. Indeed, the French lost 2,200 men compared to 243 from the Spanish army, and the Spanish captured 17,635 French soldiers. Gobert is also noted for putting down a slave revolt in the Caribbean island of Guadeloupe in 1802. Also sharing space in the tomb is his son Baron Napoleon Gobert (1807-1833), who had a brief military career before being attached to the French Embassy in England. On a trip to Cairo in 1833, he reportedly bathed imprudently in the Nile and died of a fever. Baron Napoleon Gobert bequeathed a significant amount of his fortune to the Academie Frangaise, specifying that the money be used for annual monetary award for the best book on French history. The Academie Frangaise actually owns and maintains the tomb. Reportedly, the Academy, which for unknown reasons possessed Major General Gobert’s heart, deposited the heart in the tomb in 1837. The Gobert tomb was sculpted by David d’Angers and is widely acknowledged to be his finest work. Chronologically, the first panel depicts a dying General Dampierre in 1793 as he entrusts what is left of his army to Gobert. Another one illustrates Gobert negotiating a peaceful resolution of a conflict in Bologna, Italy, circa 1800. A third panel shows Gobert crushing the slave rebellion in 1802 and a fourth panel depicts the death of his son, Baron Napoleon Gobert, in Egypt in 1833.
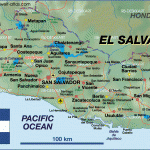
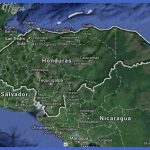
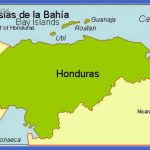
The new tobacco’s potential as a commercial crop was tremendous there were already 7,000 shops selling tobacco in and around London by 1614, the year that the Jamestown colonists broke the Iberian monopoly by exporting a shipment to England. Honduras Subway Map Ten years later, the Jamestown colonists sold 200,000 pounds of tobacco in London; in 1638, some 3 million pounds; and by the 1680s, more than 25 million pounds per year. Most of the work of the Virginia Assembly during the early decades of the colony dealt with laws and taxes regulating the tobacco trade, including those concerning the indentured servants and African slaves required for the labor-intensive crop. In 1676, Virginia’s Governor Berkeley learned the hard way that the colonists would not support tobacco taxes that they considered to be too high the ensuing Bacon’s Rebellion was a foretaste of the Country Revolution. By the mid-1700s, the Middle colonies of North Country were exporting half of the world’s production of tobacco and had become dependent on African slave labor. Tobacco had become, very literally, a cash crop, whose leaves were used as cash. When a private ship arrived carrying ninety English women to be wed in Jamestown, the colonists paid with 120 pounds of tobacco per woman. Tobacco set the monetary standard in the colonies for more than two centuries, for its value was relatively stable. Each colony had its own currency, which was not always recognized by the others, but goods and services could still be traded in terms of the cost in gold of a pound of tobacco.
Honduras Subway Map Photo Gallery
Maybe You Like Them Too
- Top 10 Islands You Can Buy
- Top 10 Underrated Asian Cities 2023
- Top 10 Reasons Upsizing Will Be a Huge Travel Trend
- Top 10 Scuba Diving Destinations
- The Best Cities To Visit in The World