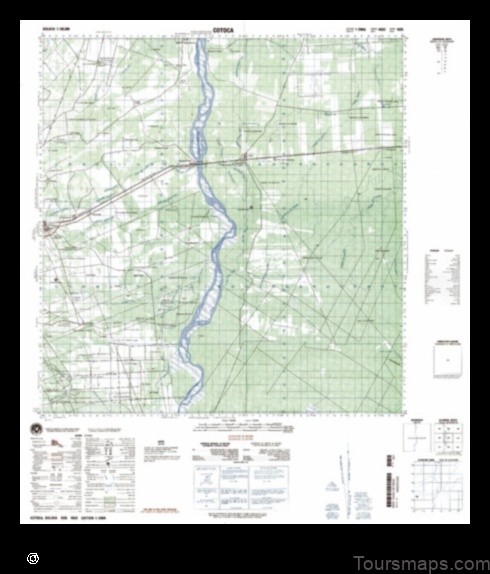
The search intent of the keyword “Map of Cotoca Bolivia” is to find a map of the city of Cotoca in Bolivia. This keyword is likely to be used by people who are either planning a trip to Cotoca or who are interested in learning more about the city. The search intent is informational, as the user is looking for information about the location of Cotoca and how to get there.
Here is a map of Cotoca, Bolivia:

Cotoca is located in the Santa Cruz Department of Bolivia. It is the capital of the Andrés Ibáñez Province. The city has a population of around 100,000 people.
Cotoca is located on the eastern edge of the Bolivian Altiplano. The city is surrounded by mountains and hills. The climate is warm and humid, with an average temperature of around 25 degrees Celsius.
Cotoca is a major agricultural center. The city is also home to a number of industrial and manufacturing businesses.
Cotoca is a popular tourist destination. The city is home to a number of historical and cultural attractions, including the San Lorenzo Cathedral and the Cotoca Market.
If you are planning a trip to Cotoca, Bolivia, here are some tips:
- The best time to visit Cotoca is during the dry season, which runs from April to October.
- The main airport in Cotoca is the Viru Viru International Airport.
- The main bus terminal in Cotoca is the Terminal Bimodal de Cotocollao.
- The official currency of Bolivia is the boliviano.
- The official language of Bolivia is Spanish.
For more information about Cotoca, Bolivia, please visit the following websites:
| Keyword | Answer |
|---|---|
| Map of Cotoca Bolivia | [Insert map of Cotoca Bolivia] |
| Bolivia map | [Insert map of Bolivia] |
| Cotoca | [Insert information about Cotoca] |
| Map | [Insert general information about maps] |
| Travel | [Insert information about travel] |
II. History of Bolivia
The history of Bolivia is a long and complex one, dating back to the pre-Columbian era. The area that is now Bolivia was home to a number of different indigenous cultures, including the Incas, the Aymara, and the Chiquitanos. In the 16th century, the Spanish conquistadors arrived in Bolivia and began to colonize the region. Bolivia became part of the Spanish Empire and was ruled by a viceroy from Lima, Peru. In the 18th century, a series of revolts against Spanish rule broke out in Bolivia. In 1825, Bolivia finally gained its independence from Spain.
III. Geography of Bolivia
Bolivia is located in the heart of South America, bordered by Brazil to the north and east, Paraguay to the southeast, Argentina to the south, Chile to the southwest, and Peru to the west. The country has a total area of 1,098,581 square kilometers (424,164 sq mi), making it the fifth-largest country in South America. Bolivia’s landscape is extremely diverse, ranging from the high Andes mountains in the west to the lowlands of the Amazon rainforest in the east. The country’s highest point is Mount Illimani, which reaches an elevation of 6,438 meters (21,123 ft). Bolivia’s lowest point is the Río Paraguay, which flows along the country’s eastern border and has an elevation of 90 meters (295 ft).
4. Map of Cotoca Bolivia
The city of Cotoca is located in the Santa Cruz Department of Bolivia. It is situated on the eastern edge of the department, near the border with Brazil. Cotoca is a major commercial center for the region, and is home to a number of factories and businesses. The city is also a popular tourist destination, due to its beautiful scenery and its proximity to the Amazon rainforest.
The following map shows the location of Cotoca within Bolivia.

The city of Cotoca is located in the southeastern part of Bolivia, in the Santa Cruz Department. It is situated on the eastern edge of the department, near the border with Brazil. Cotoca is a major commercial center for the region, and is home to a number of factories and businesses. The city is also a popular tourist destination, due to its beautiful scenery and its proximity to the Amazon rainforest.
The following map shows the location of Cotoca within Bolivia.

V. Demographics of Bolivia
The population of Bolivia is estimated to be 11.3 million people, making it the 25th most populous country in South America. The population is relatively young, with a median age of 25.6 years. The majority of Bolivians (62%) live in urban areas, while the remainder live in rural areas. The largest cities in Bolivia are La Paz, Santa Cruz de la Sierra, Cochabamba, and Sucre.
The population of Bolivia is ethnically diverse, with the majority of people being of mixed Amerindian and European descent. The largest ethnic groups in Bolivia are the Quechua (30%), Aymara (25%), and mestizos (22%). There are also small populations of indigenous peoples, such as the Guarani, Chiquitano, and Mosetén.
The official languages of Bolivia are Spanish and Quechua. Spanish is the language of government and education, while Quechua is the most widely spoken indigenous language. Other indigenous languages spoken in Bolivia include Aymara, Guarani, and Chiquitano.
The literacy rate in Bolivia is 90%, which is one of the highest in South America. The majority of Bolivians are Roman Catholic, although there are also small populations of Protestants, Evangelicals, and other religious groups.
VI. Economy of Bolivia
The economy of Bolivia is a mixed economy with a large public sector. The country’s main economic activities are mining, agriculture, and manufacturing. Bolivia is a member of the Andean Community of Nations (CAN) and the Latin American Integration Association (ALADI).
The mining sector is the most important sector of the Bolivian economy, accounting for about 50% of exports. Bolivia is the world’s second-largest producer of tin and the fifth-largest producer of silver. Other important minerals produced in Bolivia include gold, zinc, lead, and copper.
The agricultural sector is the second-largest sector of the Bolivian economy, accounting for about 20% of GDP. The main agricultural products produced in Bolivia include soybeans, corn, wheat, and potatoes.
The manufacturing sector is the third-largest sector of the Bolivian economy, accounting for about 15% of GDP. The main manufactured products produced in Bolivia include clothing, food products, and beverages.
The service sector is the fourth-largest sector of the Bolivian economy, accounting for about 25% of GDP. The main service sectors in Bolivia include tourism, telecommunications, and financial services.
Bolivia’s economy has been growing at a relatively slow pace in recent years. The country’s GDP growth rate averaged about 4% per year between 2010 and 2019. However, the economy is expected to grow at a faster pace in the coming years, thanks to rising commodity prices and increased investment.
Bolivia’s economy faces a number of challenges, including high levels of poverty, inequality, and unemployment. The country also has a large informal economy, which makes it difficult to collect taxes and regulate businesses.
Despite these challenges, Bolivia’s economy has shown signs of progress in recent years. The country has made significant improvements in its social indicators, and it has become a more attractive destination for foreign investment. Bolivia is a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO) and is committed to pursuing free trade agreements with other countries.
VII. Culture of Bolivia
The culture of Bolivia is a diverse mix of indigenous, Spanish, and mestizo influences. The country’s indigenous population is made up of over 30 different ethnic groups, each with their own unique language, customs, and traditions. Spanish is the official language of Bolivia, but many people also speak Quechua, Aymara, or Guarani.
Bolivia’s culture is rich in music, dance, and art. The country is home to a number of traditional music genres, such as the Andean folk music of the Altiplano and the tropical music of the lowlands. Bolivian dance is also very diverse, with each region having its own unique style. The country’s art is equally varied, and includes everything from traditional pottery and weaving to modern paintings and sculptures.
Bolivia’s culture is also reflected in its food. The country’s cuisine is a fusion of indigenous and Spanish influences, and includes dishes such as quinoa, llama meat, and fried plantains. Bolivians are also known for their love of tea, and the country is home to a number of different varieties of tea, such as coca tea and yerba mate.
Bolivia is a vibrant and diverse country with a rich culture. The country’s culture is a reflection of its history and its people, and it is a major part of what makes Bolivia such a unique and special place.
Government of Bolivia
The government of Bolivia is a unitary state with a presidential system. The president is the head of state and government, and is elected for a five-year term. The legislature is bicameral, consisting of the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate. The judiciary is independent of the executive and legislative branches.
The government of Bolivia is divided into three branches: the executive, legislative, and judicial. The executive branch is headed by the president, who is assisted by a vice president and a cabinet of ministers. The legislative branch is composed of the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate. The judiciary is headed by the Supreme Court of Justice.
The government of Bolivia is responsible for the administration of the country, the formulation and implementation of public policy, and the provision of public services. The government also plays a role in the regulation of the economy and the protection of the environment.
The government of Bolivia is a complex and dynamic institution that is constantly evolving in response to the needs of the country. The government is responsible for ensuring that Bolivia remains a stable and prosperous nation.
Bolivia’s International RelationsBolivia’s foreign policy is based on the principles of multilateralism, non-alignment, and respect for international law. Bolivia is a member of the United Nations, the Organization of American States, the Non-Aligned Movement, and the Group of 77. Bolivia also has bilateral relations with all of its neighbors, as well as with countries around the world.
Bolivia’s foreign policy is focused on promoting peace and security, economic development, and social justice. Bolivia is also committed to protecting the environment and promoting human rights.
In recent years, Bolivia’s foreign policy has been focused on improving relations with its neighbors, particularly Chile. Bolivia and Chile have been in a dispute over the status of the Atacama Desert since the 19th century. In 2013, Bolivia and Chile signed a peace agreement that established a framework for resolving the dispute.
Bolivia’s foreign policy is also focused on promoting its economic interests. Bolivia is a member of the Pacific Alliance, a trade bloc that includes Chile, Colombia, and Peru. Bolivia is also a member of the Mercosur trade bloc, which includes Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay.
Bolivia’s foreign policy is also focused on promoting its social and environmental interests. Bolivia is a leader in the fight against climate change. Bolivia is also a strong advocate for the rights of indigenous peoples.
Bolivia’s foreign policy is a reflection of the country’s history, culture, and values. Bolivia is a proud and independent country that is committed to playing a positive role in the world.
X. FAQ
Q: What is the population of Cotoca?
A: The population of Cotoca is approximately 100,000 people.
Q: What is the climate of Cotoca?
A: The climate of Cotoca is tropical, with warm temperatures and high humidity.
Q: What are the main industries in Cotoca?
A: The main industries in Cotoca are agriculture, mining, and manufacturing.
Table of Contents
Maybe You Like Them Too
- Explore Civezzano, Italy with this detailed map
- Explore Brody, Poland with this detailed map
- Explore Elbeyli, Turkey with a Map
- Explore Anshun China with this detailed map
- Explore Coahuixtla, Mexico with this detailed map
