I. Introduction
This document provides a brief overview of the map of Bangladesh. It covers the country’s history, geography, political divisions, climate, natural resources, culture, economy, and tourism.
II. History of the Map of Bangladesh
The first known map of Bangladesh was created by the Arab geographer Al-Idrisi in the 12th century. It showed the country as a part of the Indian subcontinent. In the 16th century, the Portuguese explorer Duarte Barbosa created a map that showed Bangladesh as a part of the Mughal Empire. In the 18th century, the British East India Company took control of Bangladesh and created a map that showed the country as a part of British India. In 1947, Bangladesh became an independent country.
III. Geography of the Map of Bangladesh
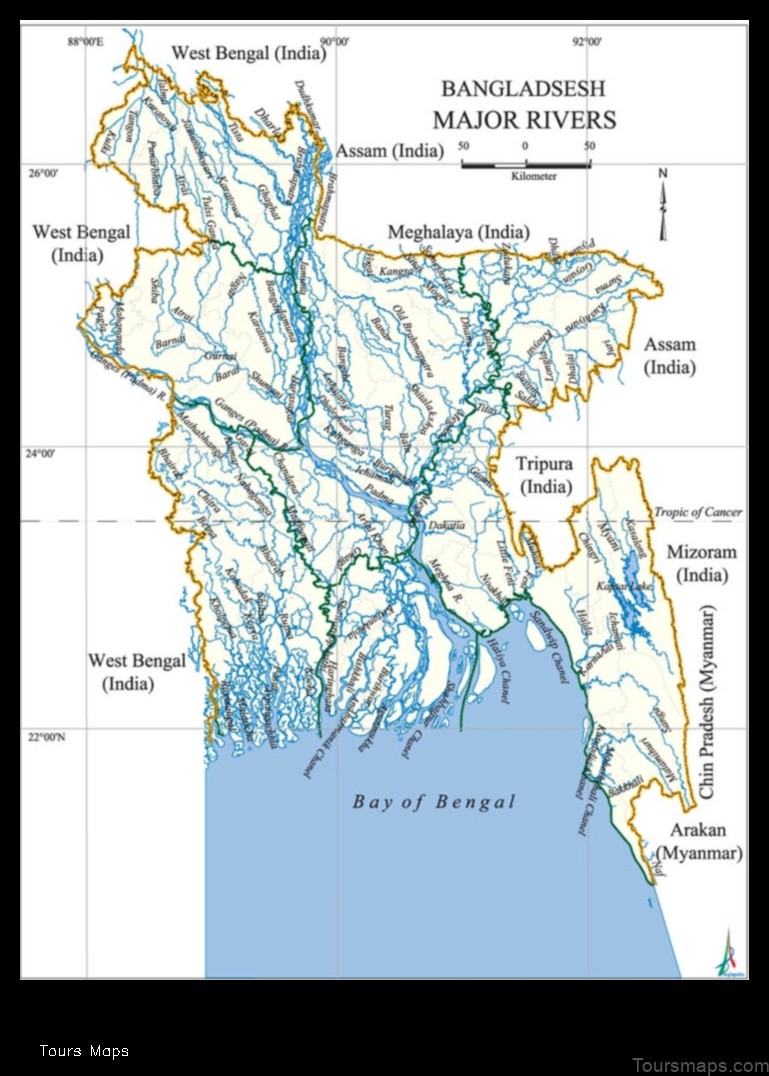
Bangladesh is located in South Asia. It is bordered by India to the west, north, and east, and by Myanmar to the southeast. The country has a total area of 147,570 square kilometers (57,040 square miles). Bangladesh is a low-lying country with an average elevation of just 12 meters (39 feet) above sea level. The country is home to a number of rivers, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna.
IV. Political Divisions of the Map of Bangladesh
Bangladesh is divided into eight administrative divisions: Dhaka, Chittagong, Khulna, Rajshahi, Sylhet, Barisal, Rangpur, and Mymensingh. Each division is further divided into districts.
V. Climate of the Map of Bangladesh
Bangladesh has a tropical monsoon climate. The summers are hot and humid, with temperatures reaching up to 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit). The winters are mild, with temperatures ranging from 10 to 20 degrees Celsius (50 to 68 degrees Fahrenheit). The country receives an average of 2,500 millimeters (98 inches) of rainfall per year.
VI. Natural Resources of the Map of Bangladesh
Bangladesh is rich in natural resources. The country has deposits of natural gas, coal, copper, gold, and silver. The country is also home to a number of forests and wildlife reserves.
Bangladesh is a diverse country with a rich culture. The country’s population is made up of a number of ethnic groups, each with its own unique culture. The official language of Bangladesh is Bengali. The country’s major religions are Islam, Hinduism, and Buddhism. Bangladesh is a developing country with a GDP of $246 billion. The country’s economy is based on agriculture, manufacturing, and services. The main exports of Bangladesh are textiles, garments, and leather goods. Bangladesh is a popular tourist destination. The country has a number of historical sites, natural attractions, and cultural events. Some of the most popular tourist destinations in Bangladesh include the Dhaka International Trade Fair, the Sundarbans National Park, and the Chittagong Hill Tracts. Q: What is the capital of Bangladesh? A: Dhaka is the capital of Bangladesh. Q: What is the population of Bangladesh? A: The population of Bangladesh is approximately 164 million people. Q: What is the official language of Bangladesh? A: The official language of Bangladesh is Bengali. Q: What are the major religions in Bangladesh? A: The major religions in Bangladesh are Islam, Hinduism, and Buddhism. Q: What is the GDP of Bangladesh? A: The GDP of Bangladesh is $246 billion. Q: What are the main exports of Bangladesh? A: The main exports of Bangladesh are textiles, garments, and leather goods. Q The history of the map of Bangladesh is a long and complex one. The region that is now Bangladesh has been inhabited by humans for thousands of years, and its borders have changed many times over the centuries. The earliest known inhabitants of the region were the Austroasiatic peoples, who arrived in the area around 2000 BC. These people were followed by the Dravidians, who arrived in the region around 1500 BC. In the 5th century BC, the region was conquered by the Mauryan Empire, which ruled over most of northern India. The Mauryans were followed by the Gupta Empire, which ruled over most of India from the 4th to the 6th centuries AD. In the 8th century AD, the region was conquered by the Pala Empire, which ruled over most of eastern India. The Palas were followed by the Sena Empire, which ruled over most of eastern India from the 11th to the 13th centuries AD. In the 13th century AD, the region was conquered by the Delhi Sultanate, which ruled over most of northern India. The Delhi Sultanate was followed by the Mughal Empire, which ruled over most of India from the 16th to the 18th centuries AD. In the 18th century AD, the region was conquered by the British East India Company, which ruled over most of India from the 18th to the 20th centuries AD. In 1947, the region was partitioned into two countries: India and Pakistan. The eastern part of the region, which is now Bangladesh, became part of Pakistan. In 1971, Bangladesh declared its independence from Pakistan. The Bangladesh Liberation War, which lasted from 1971 to 1972, resulted in the creation of the independent nation of Bangladesh. Since its independence, Bangladesh has experienced a number of political and economic challenges. However, the country has also made significant progress in terms of its development. Bangladesh is a diverse country with a rich history and culture. It is a country with great potential, and it is likely to continue to play an important role in the region and the world. The history of the map of Bangladesh is a complex and fascinating one. The region that is now Bangladesh has been inhabited by humans for thousands of years, and its borders have changed many times over the centuries. The first major civilization in the region was the Indus Valley Civilization, which flourished from around 2500 to 1900 BC. This civilization was centered in what is now Pakistan, but it also extended into what is now Bangladesh. After the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization, the region was ruled by a variety of different empires, including the Mauryan Empire, the Gupta Empire, and the Pala Empire. In the 12th century, the region was conquered by the Delhi Sultanate, and in the 16th century, it was conquered by the Mughal Empire. In the 18th century, the region was ruled by the British East India Company. In 1947, after the partition of India, the region became the independent nation of Bangladesh. The first known map of Bangladesh was created in the 16th century by the Portuguese explorer Duarte Barbosa. This map showed the coastline of Bangladesh and the major cities of the time. In the 17th century, the Dutch cartographer Joan Blaeu created a more detailed map of Bangladesh, which included information about the country’s rivers and mountains. In the 18th century, the British cartographer James Rennell created a map of Bangladesh that was used by the British East India Company to govern the country. This map was updated in the 19th century by the British cartographer William Henry Sykes. The climate of Bangladesh is tropical, with hot, humid summers and mild winters. The average temperature in January is 21°C (70°F), while the average temperature in April is 32°C (90°F). The annual rainfall is around 2,500 mm (100 in), and most of it falls during the monsoon season from June to September. Bangladesh is a country with a rich natural resource base. The country’s natural resources include: Land is the most important natural resource in Bangladesh. The country has a total land area of approximately 144,000 square kilometers (55,000 square miles). The land is fertile and supports a variety of crops, including rice, wheat, jute, and tea. Water is also a vital natural resource in Bangladesh. The country has a number of rivers, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna. These rivers provide water for irrigation, drinking, and transportation. Minerals are another important natural resource in Bangladesh. The country has deposits of coal, natural gas, and minerals such as copper, iron, and chromium. These minerals are used in a variety of industries, including the production of electricity, steel, and cement. Forests are another important natural resource in Bangladesh. The country has a total forest area of approximately 16,000 square kilometers (6,200 square miles). These forests provide a variety of benefits, including timber, fuelwood, and habitat for wildlife. Fish are another important natural resource in Bangladesh. The country has a coastline of approximately 580 kilometers (360 miles). The country’s waters are home to a variety of fish, including shrimp, crabs, and catfish. Bangladesh’s natural resources are essential to the country’s economy. The country’s natural resources are used to produce a variety of goods and services, including food, clothing, and energy. The country’s natural resources also help to support the country’s tourism industry. The culture of Bangladesh is a blend of Bengali, Indian, and Islamic influences. The Bengali language is the official language of Bangladesh, and it is spoken by the vast majority of the population. The majority of Bangladeshis are Muslims, and Islam is the official religion of the country. However, there are also significant Hindu, Buddhist, and Christian minorities. Bangladeshi culture is rich and diverse, and it is expressed in a variety of ways, including music, dance, literature, and art. Bengali music is known for its soulful melodies and rhythms, and it is often accompanied by traditional instruments such as the tabla and the sitar. Bengali dance is also very popular, and it is often performed at festivals and special events. Bengali literature is one of the richest and most vibrant in the world, and it includes works of poetry, fiction, and drama. Bengali art is also very diverse, and it includes paintings, sculptures, and textiles. Bangladeshi culture is a vibrant and dynamic part of the country’s identity. It is a reflection of the country’s rich history and diverse people. Tourism in Bangladesh is a growing industry, with the country’s natural beauty, cultural heritage, and historical sites attracting visitors from all over the world. The country has a wide variety of tourist attractions, including beaches, mountains, forests, and historical cities. Some of the most popular tourist destinations in Bangladesh include: Cox’s Bazar: Cox’s Bazar is a coastal town in southeastern Bangladesh. It is home to the world’s longest natural sandy beach, which stretches for over 120 kilometers. The beach is a popular spot for swimming, sunbathing, and surfing. Tourism in Bangladesh is growing rapidly, and the country is expected to become a major tourist destination in the coming years. Bangladesh is a country with a rich history and culture, and it offers a variety of tourist attractions for visitors from all over the world. Some of the most popular tourist destinations in Bangladesh include: Bangladesh is also a popular destination for religious tourism, as it is home to many holy sites for Muslims, Hindus, and Buddhists. Some of the most popular religious sites in Bangladesh include: Bangladesh is a safe and welcoming country for tourists, and it offers a unique and unforgettable travel experience. Q: What is the capital of Bangladesh? A: Dhaka is the capital of Bangladesh. Q: What is the population of Bangladesh? A: The population of Bangladesh is approximately 164 million people. Q: What is the official language of Bangladesh? A: The official language of Bangladesh is Bengali. Table of Contents
Topic
Answer
Bangladesh
The People’s Republic of Bangladesh is a country in South Asia. It is bordered by India to the west, north, and east, and Myanmar to the southeast. The capital and largest city is Dhaka.
Map of Bangladesh
Culture of Bangladesh
The culture of Bangladesh is a blend of Bengali, Indian, and Islamic cultures. The Bengali language is the official language of the country, and Islam is the state religion.
History of Bangladesh
The history of Bangladesh can be traced back to the early 1st millennium BCE. The region was ruled by a variety of empires and dynasties over the centuries, including the Mauryan Empire, the Gupta Empire, and the Delhi Sultanate.
South Asia
South Asia is a sub-region of Asia that comprises the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
II. History of the Map of Bangladesh
II. History of the Map of Bangladesh
II. History of the Map of Bangladesh
V. Climate of the Map of Bangladesh
VI. Natural Resources of the Map of Bangladesh
VII. Culture of the Map of Bangladesh
IX. Tourism in the Map of Bangladesh
Sundarbans: The Sundarbans is a vast mangrove forest located in southwestern Bangladesh. It is the largest mangrove forest in the world and is home to a variety of wildlife, including tigers, elephants, and dolphins. The Sundarbans is a popular destination for eco-tourism.
Chittagong: Chittagong is a port city in southeastern Bangladesh. It is the second-largest city in the country and is home to a number of historical sites, including the Chittagong Hill Tracts Museum and the Laldighi Lake. Chittagong is also a popular shopping destination.
Dhaka: Dhaka is the capital of Bangladesh and is the largest city in the country. It is home to a number of historical sites, including the National Museum and the Ahsan Manzil Palace. Dhaka is also a popular shopping destination.
X. FAQ
Maybe You Like Them Too
