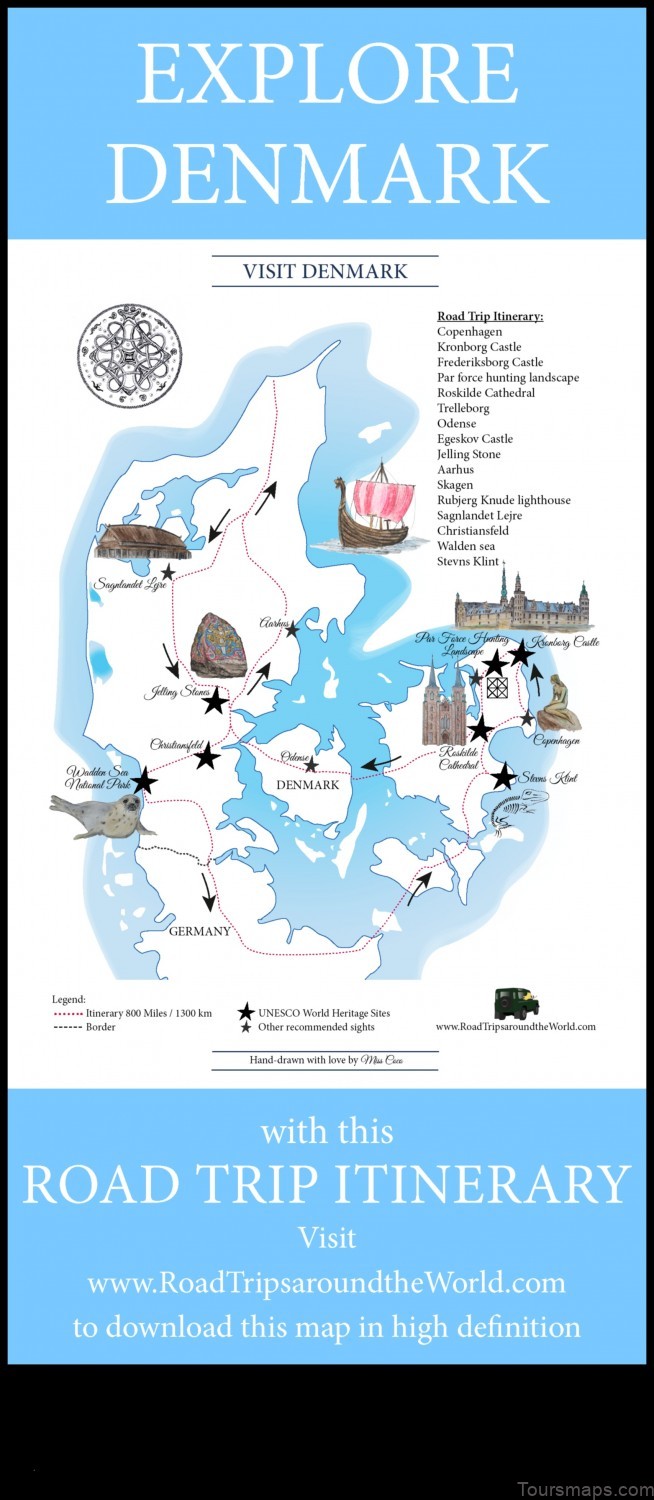
I. Map of Denmark
II. Physical Geography of Denmark
III. Political Geography of Denmark
IV. Climate of Denmark
V. Demographics of Denmark
VI. Economy of Denmark
VII. Culture of Denmark
VIII. History of Denmark
IX. Government of Denmark
X. FAQ
united states map
map of denmark and united states
denmark usa map
united states denmark map
The search intent of the keyword “Map of Denmark United States” is to find a map that shows the location of Denmark in the United States. This could be for a variety of reasons, such as:
- To plan a trip to Denmark
- To learn more about the history of Denmark
- To find out where Danish immigrants settled in the United States
- To find out what the relationship is between Denmark and the United States
The searcher is likely to be looking for a map that is easy to read and understand, and that provides information about the location of Denmark in the United States. They may also be looking for a map that includes other information, such as the names of cities and towns in Denmark, or the location of major landmarks.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Denmark | A country in Northern Europe. |
| United States | A country in North America. |
| Map of Denmark | A map that shows the location of Denmark in the world. |
| Map of United States | A map that shows the location of the United States in the world. |
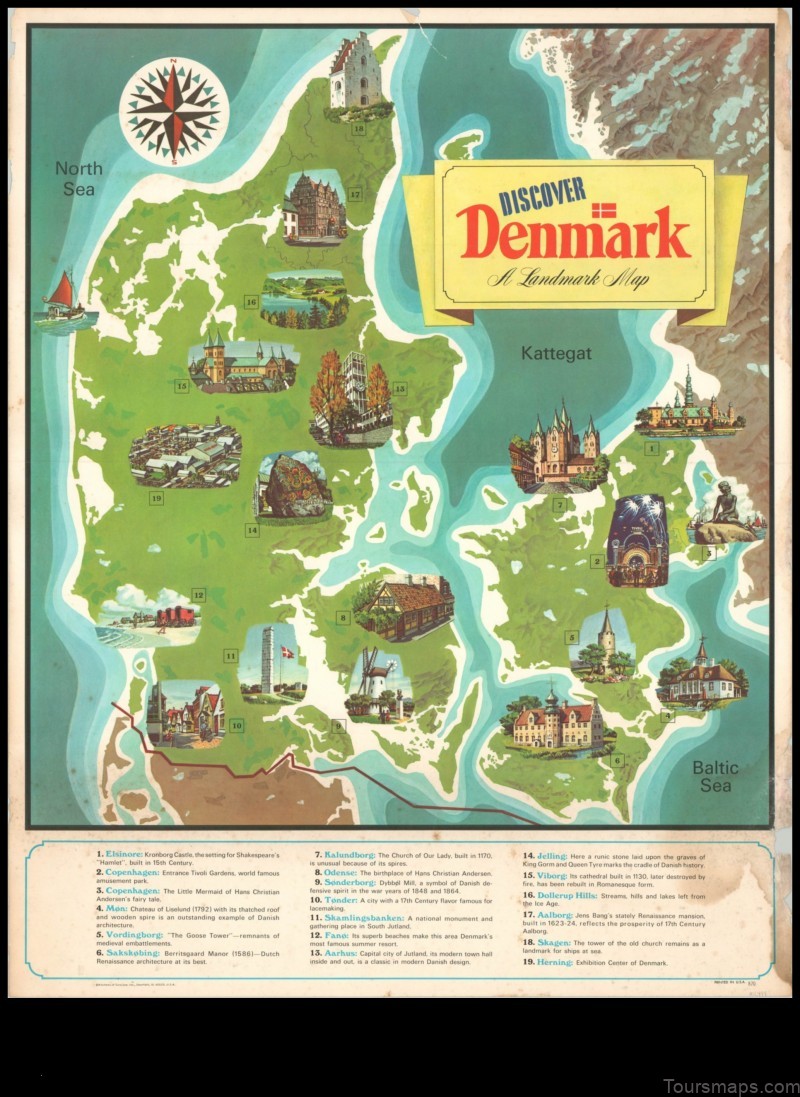
II. Physical Geography of Denmark
The physical geography of Denmark is characterized by its flat, low-lying terrain. The country is located in Northern Europe, and it borders Germany to the south. The climate is temperate, with mild winters and cool summers. The landscape is dominated by agricultural land, forests, and wetlands. The highest point in Denmark is Yding Skovhøj, which is located in the central part of the country.
III. Political Geography of Denmark
The political geography of Denmark is characterized by its unitary state structure and its membership in the European Union. Denmark is divided into five regions, each of which is governed by a regional council. The regions are responsible for a range of tasks, including healthcare, education, and transportation. Denmark is also divided into 98 municipalities, each of which is governed by a municipal council. The municipalities are responsible for a range of tasks, including local services, such as waste collection and water supply.

IV. Climate of Denmark
The climate of Denmark is temperate, with mild summers and cool winters. The average temperature in January is around 0 °C (32 °F), while the average temperature in July is around 17 °C (63 °F). The climate is influenced by the North Atlantic Drift, which brings warm water from the Gulf Stream to the coasts of Denmark.
The climate of Denmark is also affected by the prevailing winds, which are from the southwest. These winds bring warm air from the Atlantic Ocean, which helps to moderate the climate.
The amount of precipitation in Denmark varies from region to region. The west coast of Denmark receives the most precipitation, with an average of around 800 mm (31 in) per year. The east coast of Denmark receives less precipitation, with an average of around 600 mm (24 in) per year. The interior of Denmark receives the least precipitation, with an average of around 500 mm (20 in) per year.
The climate of Denmark is generally considered to be mild and comfortable. However, there are occasional periods of extreme weather, such as storms and floods.
V. Demographics of Denmark
The population of Denmark is approximately 5.8 million people. The majority of the population is Danish, with small minorities of Greenlandic, Faroese, and German people. The official language of Denmark is Danish, but Greenlandic and Faroese are also recognized as official languages in Greenland and the Faroe Islands, respectively.
The majority of the population of Denmark lives in urban areas. The largest city is Copenhagen, which has a population of over 1 million people. Other major cities include Aarhus, Odense, and Aalborg.
The economy of Denmark is one of the most developed in the world. The country has a high standard of living and a strong social welfare system. The main industries in Denmark include manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism.
Denmark is a member of the European Union and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). The country is also a founding member of the United Nations.
II. Map of Denmark
The map of Denmark shows the country’s location in Northern Europe. It is bordered by Germany to the south, Sweden to the east, and the North Sea to the west. The country has a total area of 43,094 square kilometers (16,639 sq mi), making it the 13th largest country in Europe.
Denmark is a unitary state with a parliamentary system of government. The capital and largest city is Copenhagen. The official language is Danish, which is spoken by the majority of the population. Other languages spoken in Denmark include German, English, and Turkish.
Denmark has a population of approximately 5.8 million people. The population is concentrated in the southern part of the country, with the largest cities being Copenhagen, Aarhus, and Odense.
Denmark is a developed country with a high standard of living. The economy is based on services, industry, and agriculture. The main exports are machinery, pharmaceuticals, and food products.
Denmark is a member of the European Union, the United Nations, and NATO. The country is also a founding member of the Nordic Council.
VII. Culture of Denmark
The culture of Denmark is a blend of Scandinavian, Germanic, and Nordic influences. It is characterized by its strong sense of community, its love of nature, and its emphasis on social welfare.
Danish culture is heavily influenced by its Viking heritage. The Vikings were a seafaring people who explored and settled much of Northern Europe. They brought with them their own unique culture, which included a strong sense of community, a love of nature, and a belief in the importance of social welfare.
Today, Denmark is a modern, industrialized country. However, its culture still retains many of its traditional values. Danes are known for their strong sense of community, their love of nature, and their commitment to social welfare.
One of the most important aspects of Danish culture is the concept of hygge. Hygge is a Danish word that means “coziness” or “warmth”. It is a feeling of contentment and well-being that is often associated with spending time with loved ones, enjoying simple pleasures, and being in nature.
Another important aspect of Danish culture is the emphasis on social welfare. Denmark has a strong social safety net that provides its citizens with access to free healthcare, education, and childcare. This allows Danes to feel secure and confident about their future, which contributes to their sense of well-being.
Danish culture is a unique and vibrant blend of tradition and modernity. It is a culture that is constantly evolving, but it always retains its core values of community, nature, and social welfare.
History of DenmarkThe history of Denmark can be traced back to the Stone Age, when the first humans settled in the area. The country was first united under a single ruler in the 9th century, and it became a major power in the Middle Ages. Denmark was a leading member of the Hanseatic League, and it played a significant role in the Protestant Reformation. In the 18th century, Denmark was ruled by the House of Oldenburg, and it became a major European power. However, the country suffered a series of military defeats in the 19th century, and it lost Norway to Sweden in 1814. In the 20th century, Denmark was neutral during World War I, but it was occupied by Germany during World War II. After the war, Denmark became a member of the United Nations and the European Union.
IX. Government of Denmark
The government of Denmark is a parliamentary democracy. The head of state is the Queen, who is represented by the Prime Minister. The legislature is the Folketing, which is made up of 179 members. The judiciary is independent of the executive and legislative branches.
The government of Denmark is responsible for a wide range of functions, including:
- Defence
- Foreign policy
- Education
- Healthcare
- Social welfare
The government of Denmark is funded by taxes, which are levied on individuals, businesses, and goods and services.
The government of Denmark is a member of the European Union and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
FAQ
Q: What is the capital of Denmark?
A: Copenhagen
Q: What is the population of Denmark?
A: 5.8 million
Q: What is the official language of Denmark?
A: Danish
Table of Contents
Maybe You Like Them Too
- Explore Doncaster, United Kingdom with this detailed map
- Explore Arroyito, Argentina with this Detailed Map
- Explore Belin, Romania with this detailed map
- Explore Almudévar, Spain with this detailed map
- Explore Aguarón, Spain with this detailed map
