Swedish painting is notable particularly for the interior decoration of Kalmar Castle and the Palace in Stockholm (by J. B. van Uther) and the work of Holger Hansson (fl. 1586-161 9), Ottomar Elliger the Elder (1 633-79), Johan Sylvius (d. 1 695), the Hamburg artist David Klockervon Ehren-strahl (1629-98), the Flemish family of van Mytens or Meytens, Alexander Roslin (1718-93), Gustaf Lundberg (1696-1796) and C. G. Pilo (1711-93). Among Danish painters were Jakob Binck (born c. 1500), Hans Knieper (d. 1587) of Antwerp and Karel van Mander (1605-70).
Classical-style architecture left its mark on Copenhagen in the range of buildings linking the Amalienborg palaces, by Kaspar Fredrik Harsdorff (1735-99) and his pupil Christian Fredrik Hansen (1756-1845). Building took place from 1794 onwards.
Theophil Hansen (1813-91), a representative of the school known as His-toricism (neo-classicism), designed Athens University and some imposing buildings on the Ring in Vienna. Martin Nyrop (1 849-1 921) builttheTown Hall in Copenhagen, and together with Peter Vilhelm Jensen-Klint (1853-1930: Grundt-vig Church, Copenhagen) developed new architectural forms. M. G. Bindesboll (1800-56) designed the Thorvaldsen Museum to house the work of Bertel Thorvaldsen (1770-1844), Denmark’s greatest sculptor, who ranks with Antonio Canova and Asmus Jakob Carstens as a representative of the ideals of neo-classicism in their purest form but also displays the weaknesses of the style; among his finest works is the figure of Christ in the Church of Our Lady in Copenhagen. Other sculptors of the period were H. V. Bissen (1798-1868) and J. A. Jerichau (1816-83).
Notable examples of Swedish architecture are the Old Opera House (by F. Adelcrantz, 1716-96), the Exchange (by E. Palmstedt, 1741-1803) and the interior of the Palace (by C. HSrlemann, 1700-53), all in Stockholm. Sculptors included, in addition to J. T. Sergei, J. N. Bystrom (1783-1848), B. E. Fogelberg (1786-1854) and Per Hasselberg (1850-94).
Norway produced very fine work in the field of folk art, which indeed flourished throughout Scandinavia, notable in the rustic rose painting. The heyday of rustic painting in southern Sweden was between 1750 and 1850 (Dalarna, Gas-trikland, Helsingland). The painted wall hangings produced mainly for festive occasions were mostly of cloth or paper; wall and ceiling painting was practised in the north.
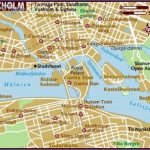
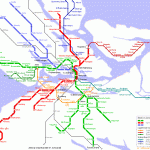
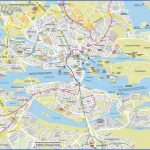
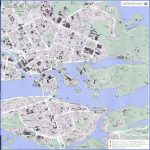
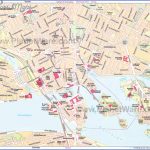
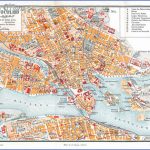
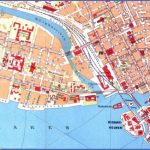
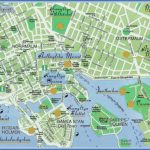
Stockholm Map Photo Gallery
Maybe You Like Them Too
- The Best Cities To Visit in The World
- World’s 10 Best Places To Visit
- Coolest Countries in the World to Visit
- Travel to Santorini, Greece
- Map of Barbados – Holiday in Barbados