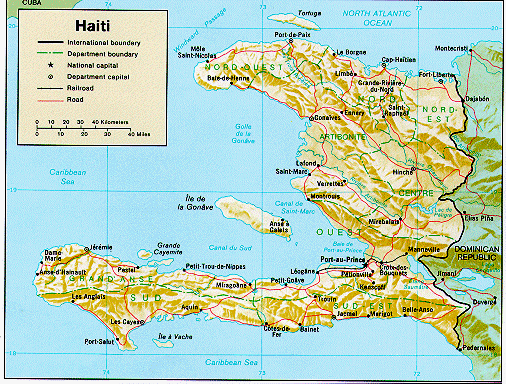
The Haitian Revolution, 17901804 The tremors of the French Revolution, starting in 1789, tempted different social groups in Saint-Domingue to improve their position. Italy Map Analogous to the French National Assembly, an assembly of the free people of the colony was allowed. Still, to what degree the free colored people should participate remained controversial. Completely excluded by the grands blancs, the affranchis revolted, to no avail, in 1790. When, on the other hand, the French government tried to pacify the mulattos by granting civil rights to the wealthiest among them in 1791, the whites objected and fighting flared up again. More seriously, a slave rebellion broke out in August, involving up to 80,000 slaves by November. To obtain allies against the rebellion, the government gave civil rights to all affranchis in 1792. But the disintegration of the country continued, especially when, in 1793, French, Spanish, and British forces arrived. Different factions of the rebels allied with different European powers. The former slave Toussaint L’Ouverture joined the slave revolt sweeping the French colony of Saint-Domingue (later Haiti) in 1791. He rose to a position of power and ultimately led the nation to independence making it the first in Latin Country to attain that status. (Bibliotheque Nationale, Paris, France/Roger-Viollet, Paris/Bridgeman Art Library)
Even under the trade imbalance, however, many colonial businesses prospered, and, even under the yoke of mercantilism, many colonists began leaning toward self-sufficiency by making products in their homes. Milan Map In order to protect the sale of English-made goods, Parliament passed laws that restricted manufacturing in the colonies. Colonists were allowed to make goods for their own personal use, but they were prohibited from selling these goods anywhere else, including England or any other colony. In 1699, for example, Parliament passed the Woolen Act, which prohibited the colonies from sending wool to England or to other colonies. The Iron Act (1750) kept the colonists from making their own iron. Because of this act, the colonists had to send their raw iron to England and buy finished iron products from English iron mills. Trade made the colonies what they were: agricultural centers, commercial centers, and, overall, industrious centers. The mercantile system worked well for England. It provided ready markets for English-made goods, and it supplied the mother country with raw materials not available in England. It was no wonder that England spared no expense in the defense of the colonies during the French and Indian War or that England could not stand to lose the North Country colonies during the Country Revolution.
Despite his stellar record and the patronage of Cumberland, Wolfe had few opportunities once the War of the Austrian Succession ended in 1748. Haiti Metro Map Although he was a solid member of the establishment because of his family connections, Wolfe did not have the financial resources or the aristocratic weight to secure a command. Instead, he ran day-to-day operations for Edward Cornwallis, the absentee colonel of the 20th Foot, who was lieutenant governor of Nova Scotia. In his free time, Wolfe studied classical military treatises and new drill books from Prussia, being particularly fascinated by the new tactic of using mixed skirmishers against columns of troops, which he experimented with in the training of his own regiment.
Haiti Metro Map Photo Gallery
Maybe You Like Them Too
- Top 10 Islands You Can Buy
- Top 10 Underrated Asian Cities 2023
- Top 10 Reasons Upsizing Will Be a Huge Travel Trend
- Top 10 Scuba Diving Destinations
- The Best Cities To Visit in The World